Which software QA KPIs offer real insight—not just numbers? How can they help you prevent defects, improve processes, and align testing with business goals? Track software quality KPIs that reveal root causes, guide strategy, and boost decision-making clarity, hand in hand with Abstracta.


Key Software QA Key Performance Indicators are essential metrics used to assess the quality, performance, and efficiency of software testing processes. These indicators help identify critical issues in production, evaluate user experience, measure automation impact, and guide continuous improvement strategies across the software development lifecycle.
No matter if you’re a leading enterprise or a startup taking its first steps, software quality can make or break your users’ trust, brand reputation, and bottom-line performance. Tracking the right software Quality Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is the true dividing line between costly setbacks and scalable growth.
In this article, we explore how measuring QA KPIs helps organizations demonstrate the impact of testing on delivery speed, product quality, and defect reduction.
Looking to strengthen your QA strategy with actionable insights?
We help teams track the right metrics, improve test coverage, detect defects earlier, and optimize their software testing process with tailored solutions.
Explore our QA services.
Why Measure Software QA KPIs
What gets measured gets understood, but only if you’re measuring what matters. In quality assurance, tracking the right software QA KPIs allows you to connect technical insights to business outcomes. These indicators serve as anchors for visibility, enabling test managers and QA teams to make data-informed decisions that improve testing efficiency and product reliability.
It’s common for clients to suggest what they think needs fixing. But more often than not, the visible symptoms aren’t the root cause. There exist several useful tools, and when paired with a focused QA KPI framework, they can transform scattered testing efforts into strategic progress.
Metrics vs KPIs: Unlocking the True Value of Software Testing Metrics
Software Testing Metrics: The Foundation of Insight
Software Testing metrics are raw, objective data points that provide detailed insights into the software development and testing lifecycle. Examples include the number of test cases executed, defect density, and code coverage. These metrics enable teams to monitor progress, identify trends, and address inefficiencies, fostering continuous improvement.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): The Strategic Lens
KPIs go beyond operational data to assess the impact of testing efforts on broader business objectives. They measure outcomes like accelerated release cycles, reduced production defects, and enhanced user satisfaction. By aligning with organizational goals, KPIs evaluate performance and ensure testing efforts contribute to meaningful value.
On balance, metrics inform by offering granular snapshots of activity, while KPIs evaluate by providing the strategic context needed to assess success. Together, they are indispensable tools for understanding whether testing efforts are both active and impactful.
Key Software QA KPIs
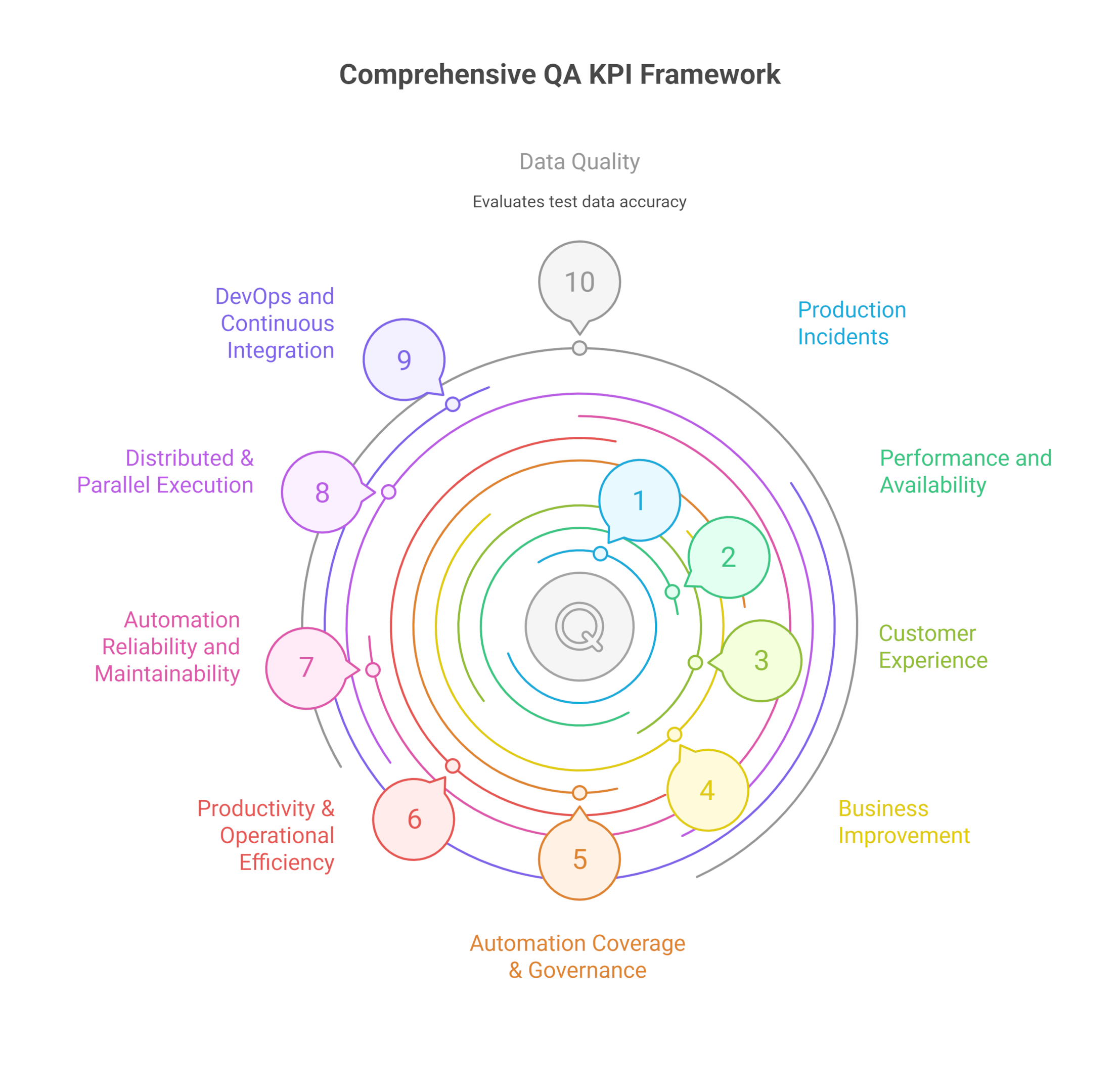

We’ve organized the following metrics by impact, starting with those tied to production incidents, a priority for most organizations. Once stability is addressed, teams can shift focus toward enhancing overall software quality attributes, testing processes, increasing test automation coverage, and deepening observability and UX.
Use this reference to identify which Quality KPIs best match your testing goals:
1. KPIs Related to Production Incidents
Production incident KPIs measure how often and how severely bugs reach end users. Metrics like incident recurrence rate, rate of incidents per release, and Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR) help identify testing gaps and prioritize fixes that reduce costly disruptions in live environments.
2. KPIs for Performance, Availability, Service-Level Indicators
Performance and availability KPIs track system speed and uptime. Common metrics include average response time, error rate, and SLA compliance. Monitoring them helps QA teams prevent bottlenecks and enable a smooth experience across all environments and user loads.
3. KPIs for Digital Experience & Customer Experience
Customer experience KPIs connect QA impact to user satisfaction. Metrics like CSAT, NPS, APDex, user friction rate, and error frequency in key flows reveal how software quality influences user trust, retention, and brand perception across digital experiences.
4. KPIs for Business Value & Business Improvement
Business-focused KPIs link QA to financial outcomes. Examples include cost per defect, test ROI, and time-to-market. These metrics support strategic decisions and demonstrate how quality assurance drives product profitability and sustainable growth.
5. KPIs for Automation Coverage & Autonomous CI/CD Tasks
Automation coverage KPIs show how much of the application is tested automatically. Tracking test execution frequency, coverage percentage, automation reliability, autonomous pipeline tasks, and gap areas helps scale QA efforts and improve testing governance in CI/CD pipelines.
6. KPIs for Productivity & Operational Efficiency
Productivity KPIs reflect how efficiently software testers and the entire QA team operate. Metrics like test cases executed per sprint, defects found per release, and rework rate uncover bottlenecks and support continuous improvement in test cycles and delivery speed.
7. KPIs for Automation Reliability and Maintainability
These KPIs assess the stability and upkeep of test automation. Common metrics include flaky test rate, false positives, and script maintenance time. High reliability enables trust in automation and reduces manual overhead.
8. KPIs for Distributed & Parallel Execution
KPIs for distributed testing measure how well test execution scales across environments. Useful metrics include parallel test success rate, average execution time, and latency between test nodes in complex or microservice-based systems.
9. KPIs for DevOps and Continuous Integration
These KPIs measure QA’s integration within CI/CD workflows for DevOps. Metrics such as build success rate, test duration per pipeline, and failed integration frequency highlight automation health, and boost quality gates are effective at scale.
10. KPIs for Data Quality
Data quality KPIs evaluate the accuracy and completeness of test data. Tracking data-related defects, environment sync issues, and test coverage gaps supports reliable action plans and reduces false negatives caused by incomplete or outdated data.
Many metrics listed here are industry standards, but their definitions may vary depending on organizational context. When used strategically, QA KPIs turn testing data into a roadmap for faster releases, fewer bugs, and smarter decisions.
At Abstracta, we approach Software QA KPIs as a strategic tool to validate quality, guide continuous improvement, and demonstrate the value of QA efforts to business stakeholders.
Book a meeting to dive deep into each KPI and understand how we can help you
Strategic Use of QA KPIs
To help you translate metrics into action, here’s a table that summarizes what each KPI category measures and how it can guide better decisions:
| KPI Category | What It Measures | Use This KPI To… |
|---|---|---|
| Production Incidents | Live bug frequency and resolution time | Prioritize fixes, reduce regressions, and improve incident response |
| Performance & Availability | System speed, uptime, and error rates | Identify bottlenecks before release, enable SLA compliance |
| Customer Experience | User satisfaction and journey quality | Align test focus with UX pain points and loyalty drivers |
| Business Improvement | QA impact on costs, business value, and delivery timelines | Justify QA investments, optimize release cadence |
| Automation Coverage & Autonomous CI/CD Tasks | Scope and reliability of test automation and autonomous tasks | Spot coverage gaps, scale testing safely |
| Productivity & Operational Efficiency | QA throughput and workflow blockers | Improve sprint velocity and defect detection efficiency |
| Automation Reliability & Maintainability | Test flakiness and maintenance effort | Detect brittle tests early and reduce manual interventions |
| Distributed & Parallel Execution | Parallel test success across environments | Optimize infrastructure usage and test runtime |
| DevOps & Continuous Integration | QA integration in CI/CD pipelines | Detect pipeline weak spots and stabilize releases |
| Data Quality | Accuracy and completeness of test data | Prevent false test results, improve data integrity ®ulatory compliance |
Test Coverage Approach


While many QA metrics are considered industry standards, each organization may interpret them differently. That’s why we adapt our measurement strategy to fit the system architecture, business goals, and QA maturity level of each team.
Expanding test coverage doesn’t always improve quality. What makes the difference is identifying which scenarios pose the highest risk and aligning the test strategy to those critical paths.
QA KPIs only make sense when framed within a maturity context. Without understanding where a team stands, it’s impossible to define which metrics are useful today and which should guide future improvements.
Collecting more metrics does not increase visibility. A well-designed KPI set is narrow, relevant, and directly linked to actionable insights across teams and roles.
Elements That Define Your Software QA KPIs Roadmap
- Maturity model alignment
Understanding your team’s QA maturity is essential for setting realistic goals and selecting meaningful metrics. Whether you’re stabilizing test basics or expanding automation, maturity stages shape what’s relevant. KPIs should align with current capabilities and expose gaps worth closing, not replicate frameworks built for different organizational realities. - Technology stack
Coverage decisions depend on the technical landscape. Microservices, monoliths, APIs, and mobile apps require different validation strategies. If critical layers go untested due to tooling mismatches, risks increase silently. Your test approach must reflect where value flows and where failures are most likely to occur in your stack. - Team roles and skills
Job titles reveal little about what teams can actually execute. It’s crucial to assess technical depth, scripting ability, exploratory thinking, and business alignment across QA contributors. This clarity allows for selecting metrics that reflect true strengths, such as test case quality, automation resilience, or defect traceability. - Leadership model
Leadership influences how testing is perceived and funded. When quality is viewed as a team-wide enabler, metrics shift from checklist compliance to strategic insight. Effective leaders don’t just support QA—they integrate it into planning, delivery, and review cycles, giving KPIs relevance in broader decision-making. - Software development process
Testing cadence should reflect how software is built. In CI/CD pipelines, fast feedback and early breakpoints matter more than exhaustive reports. In staged delivery models, broader coverage and milestone gates are prioritized. QA metrics must adapt to the real delivery flow—not an idealized one. - Organizational quality mindset
Quality becomes sustainable when it’s treated as a shared value, not a department. QA coaches and advocates can shape habits, but lasting change happens when product owners, developers, testing engineers, and ops teams actively support quality outcomes. KPIs should reflect this shift: fewer late defects, better collaboration, stronger delivery confidence.
How to Select the Right Software QA KPIs for Your Context


Not all KPIs are created equal. The most effective QA metrics are those aligned with your team’s goals, testing phase maturity, and business needs. Here’s how to identify them:
1. Map Software Quality to Business Impact
Start by identifying how software quality affects your customers and stakeholders:
- Is downtime affecting sales or user experience?
- Are critical defects reaching production?
- Is the development team struggling to resolve defects efficiently?
This step shifts your focus from surface metrics to strategic quality indicators that influence software development success.
2. Investigate Before You Quantify
Use tools like the 5 Whys or Ishikawa diagrams to uncover root causes before defining metrics. For instance, tracking the total number of defects may be less useful if you aren’t distinguishing between escaped defects and active defects within a cycle.
3. Prioritize KPIs by Risk and Value
With a Risk-Based Testing (RBT) mindset, assign weight to metrics that highlight critical issues:
- If uptime is essential, track defect leakage, mean time to recovery, and defect density.
- If delivery speed matters, emphasize testing cycle length, test execution rates, and testing efficiency.
- If user experience is the priority, consider failed test cases, Apdex scores, and test reliability.
4. Align KPIs with Team Maturity
Early-stage teams may focus on passed tests and the number of tests executed. Mature QA processes may track defect removal efficiency, test automation coverage, or defect detection effectiveness.
5. Aligning QA Metrics with Product Goals and Maturity Models
QA metrics are most effective when aligned with product goals and the QA maturity model, fostering collaboration and driving improvement. By adapting metrics to organizational context, connecting roles to shared objectives, and using the maturity model to guide growth, teams can achieve impactful results and elevate product quality.
6. Check if Metrics Serve All Stakeholders
QA metrics should support the entire software testing process. Test managers, development teams, and leadership should be able to interpret them. That means:
- Consistent definitions of terms like “defects found” or “test cases executed.”
- Clear dashboards that show test coverage trends and quality assurance progress.
7. Continuously Review and Adjust
Your QA KPIs should evolve with your product. If a metric is no longer helping guide decisions, it’s time to revise or replace it. Consider how tracking QA KPIs over time correlates with failed tests, customer satisfaction, or test case effectiveness.
8. Connect Manual Testing Insights to KPIs
Manual testing is key to uncovering high-risk issues, especially in complex user flows. Use software testing metrics that reflect the outcomes of these testing tasks. This allows quality assurance teams to translate manual insights into measurable improvement.
9. Link Each KPI to a Broader Quality Assurance Strategy
Quality assurance KPIs work best when tied to strategic goals. Each KPI category should support your roadmap, helping transform testing outcomes into decisions that benefit delivery speed, risk reduction, or user satisfaction.
In a Nutshell
Tracking KPIs over time allows teams to assess the evolution of their testing maturity and make informed decisions to continuously improve software outcomes. Quality metrics offer visibility into how well the development process supports business goals and customer expectations.
On the whole, product quality is a shared responsibility across the entire software development lifecycle. Developers, testers, product managers, designers, and operations all contribute to the end result. Quality assurance plays a strategic role not just in finding bugs but in maximizing business value while minimizing risk, aligning quality practices with broader organizational outcomes.
FAQs about Software QA KPIs

What are Software QA KPIs?
Software QA KPIs are metrics that track quality assurance performance. They cover test coverage, defect detection, testing efficiency, and impact. These indicators guide testing efforts and improve decision-making.
How Do QA Metrics Support the Software Testing Process?
They provide data to understand test effectiveness, test execution progress, and defects found, helping teams optimize their testing efforts and improve quality.
How Do QA Metrics Support the Software Testing Process?
QA metrics offer data-driven insights into test effectiveness, execution progress, and defect trends. These indicators help teams refine testing strategies and elevate software quality.
Which KPIs Are Most Important for Test Managers?
Key QA KPIs include test case effectiveness, defect leakage rate, pass/fail ratio, and defect density per release. These metrics reveal quality trends and guide continuous improvement.
What Is Defect Removal Efficiency?
Defect removal efficiency (DRE) measures the percentage of defects detected before release versus the total identified later. It reflects the strength of pre-release testing.
How Do You Track Testing Efficiency?
Testing efficiency is tracked by analyzing executed test instances, time spent per phase, and coverage achieved versus planned. This reveals testing depth and productivity.
What Is Test Automation Coverage?
Test automation coverage shows the percentage of test cases or scenarios executed by automated scripts. It supports faster feedback loops and reduces manual effort.
Why Is Test Case Effectiveness Important?
Test case effectiveness indicates how well tests identify actual defects. High effectiveness reflects strong test design and better defect prevention across cycles.
How Can QA KPIs Improve the Software Development Process?
QA KPIs highlight quality gaps, align testing with business goals, and surface bottlenecks early. This data-driven approach supports faster, more reliable releases.
What Is Defect Density?
Defect density calculates the number of defects per unit of code or functional area. It helps prioritize remediation efforts by identifying high-risk components.
What Should QA Teams Focus on in Early Testing Phases?
In early stages, QA teams should focus on test case design, environment readiness, and early defect detection. This foundation accelerates feedback and reduces late-stage issues.
How We Can Help You

With over 16 years of experience and a global presence, Abstracta is a leading technology solutions company with offices in the United States, Chile, Colombia, and Uruguay. We specialize in software development, AI-driven innovations & copilots, and end-to-end software testing services.
At Abstracta, we help testing teams move from isolated QA metrics to decision-enabling insights. Whether you need to stabilize your releases, scale automated tests, or define a cost-effective testing process, we partner with you to implement KPIs that reflect the true health of your software quality.
We believe that actively bonding ties propels us further and helps us enhance our clients’ software. That’s why we’ve built robust partnerships with industry leaders Microsoft, Datadog, Tricentis,
Perforce BlazeMeter, and Saucelabs to provide the latest in cutting-edge technology.
Empower your teams with expert guidance in KPIs!
Take our software testing maturity assessment and check our solutions!

Follow us on LinkedIn & X to be part of our community!
Recommended for You
What is Data Observability? From Chaos to Clarity
15 Top API Testing Tools for 2025: Features, Pricing & Use Cases
Better Your Strategy with This Software Testing Maturity Model
Tags In
Related Posts
Quality Sense Podcast: Alon Girmonsky – Testing Microservices with UP9
Challenges of testing microservices and why we need observability In this episode of Quality Sense, host, Federico Toledo intervews Alon Girmonsky, an accomplished, multi-time entrepreneur and technology leader. He’s a passionate engineer who loves building developer tools and companies. Today, he’s the CEO and co-founder…
Data Strategy in Financial Services: From Compliance to Reliable Decision-Making
Most strategies in finance fall short. This guide shows how to build a data strategy that supports AI, strengthens compliance, and creates measurable business value. A data strategy in financial services defines how institutions turn raw data into reliable, traceable insights. It aligns governance with…
Search
Contents
Categories
- Acceptance testing
- Accessibility Testing
- AI
- API Testing
- Development
- DevOps
- Fintech
- Functional Software Testing
- Healthtech
- Mobile Testing
- Observability Testing
- Partners
- Performance Testing
- Press
- Quallity Engineering
- Security Testing
- Software Quality
- Software Testing
- Test Automation
- Testing Strategy
- Testing Tools
- Work Culture





