Our method for improving test coverage over multiple test cycles
We want to test as much code as humanly (or mechanically) possible right? Yes and no. For each test cycle, it’s important to consider multiple strategies for measuring test coverage and to put a system into place where it can be maximized in the long-term as well.
Test coverage is one of the measurements of test quality that tells us how much of the application under test has been tested. As I explained in a past post, it’s a little bit like sweeping the floors of a home. When I sweep my house, I always forget to sweep some part, like the upstairs bathroom, so my sweep coverage fails to include that room. Imagine if I only included sweeping bedrooms for my sweep coverage criteria. With that criteria, if I swept 100% of the bedrooms, would that mean that the whole house is clean? No, because I completely missed the kitchen, dining room, bathrooms, etc! Therefore, we must always be careful with test coverage and recognize that sometimes it has its limitations.
We find test coverage useful for defining certain entities of the system with the intent to cover them with tests. It also tells us when we have tested sufficiently, gives us ideas of what else to test (thus expanding coverage), and helps us know quantitatively the extent of our tests. It’s a great measuring stick, but
[tweet_box design=”default” float=”none”]Even with 100% coverage we will never be guaranteed that our application is bug-free.[/tweet_box]
It’s also important to note that the percentage of test coverage isn’t everything. Even if you only managed to achieve 20% coverage, it wouldn’t be a bad thing because the ideal amount of test coverage should be determined after running a risk analysis and should be in line with your priorities.
There are many ways to consider test coverage. Here I am going to look at code coverage, data-oriented coverage, and the plethora of other techniques at a tester’s disposal.
Code Coverage
Code coverage is the most popular metric for measuring coverage. There are different levels- not only lines of code covered, but there are also branches, decisions inside logic constructors, etc.
Data-Oriented Coverage
With data-oriented coverage, you have input and output parameters, each of them having their own domain (the spectrum of possible values they can have) and if you think about all the possibilities, you see you end up with a cartesian product (because you can test every possible combination). On the other hand, you can test less and go with “each choice” coverage, which means that you choose at least each possible value at least once. There is also all-pairs, which is empirically said to have the best cost-benefit relationship, being the best mix between each-choice and all combinations.
Other Kinds of Coverage
In addition to those previously mentioned, there are several more ways to cover the product that you are testing such as state-machines, decision tables, decision trees, equivalence partition, and boundary values, etc. It’s very interesting to see that each technique is supported by an “error theory”. The error theory takes into account the typical errors that programmers commit, as for example, equivalence partition and boundary values consider the error of, for example, using a “<” instead of a “<=”, misunderstanding business logic, or for example, decision tree tries to execute all the “decisions” and combinations of interesting conditions that a program has, which is nothing more than trying to maximize the branch coverage in the code.
For me, the last point mentioned about black box is very interesting: a coverage criterion with a very black-box vision can actually improve upon white-box testing in terms of coverage.
Additionally, there are other kinds of test coverage that are not related to lines of code or inputting test data. One thing we must cover is mobile fragmentation: are we covering the main mobile devices, operating systems, and screen sizes? When it comes to browsers and operating systems, we must consider how will our web system behaves in any combination of operating systems and browsers and how many combinations we should try. Lastly, think about the test environment, the context, etc.
Laying Out the Plan
What happens when you never have enough time to reach certain criteria for your test cycles? Here I’ll present a solution that works well in these instances. I have used it before and I hope it makes sense for you too.
To illustrate the main idea, say we have different features to test on different browsers and we have organized different test cases with different test suites, each one with its own priority. We need to execute the most critical against all browsers, but the rest, we can decide to execute on a different browser. In the following test cycles, we can exchange all pairs (suite/browser). That way, in each test cycle we do not have great coverage, but after multiple test cycles, we improve it. We cannot ever be assured that we are done with testing, but when time is scarce, we have to use it wisely and do our best to reduce risk.
Here’s an example of how to plan good test coverage over many test cycles.
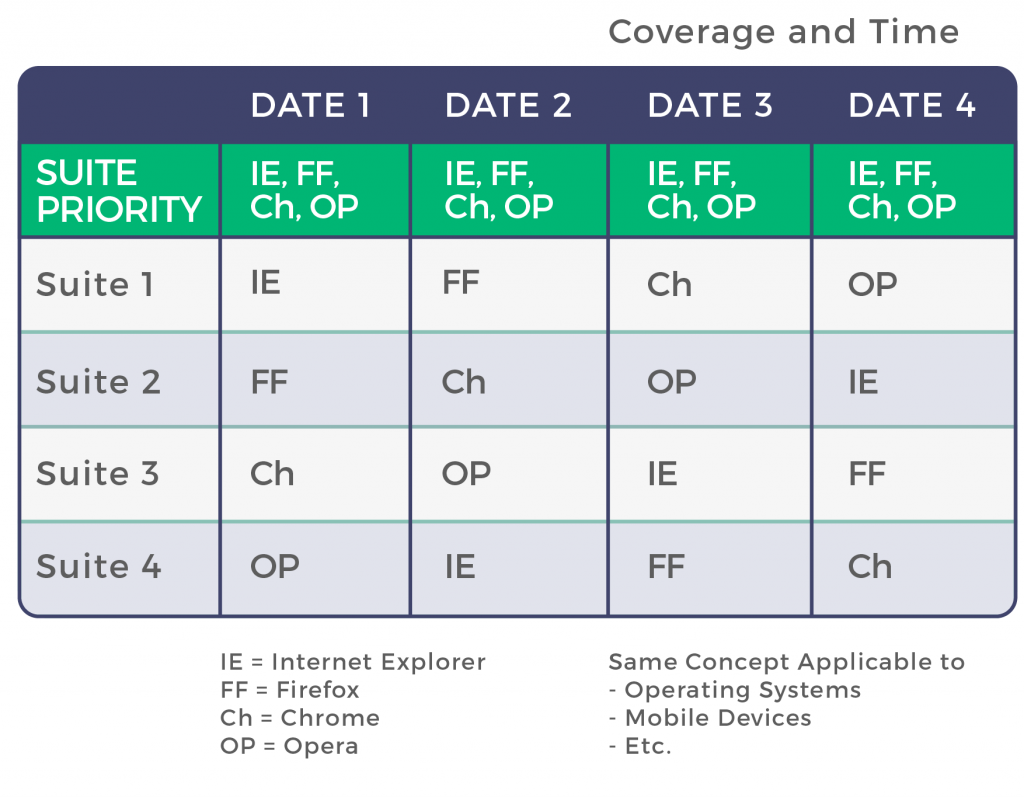

Where it says “date 1”, it could also say “sprint 1”, “iteration 1”, “day 1”, “version 1”, etc. The goal here is to distinguish which test cases you will execute in each iteration in each environment. For some of them, it is mandatory to execute test every time on all browsers (probably the most critical ones). Others can be divided into groups and executed only in one browser, but in a very clever way in order so that each is executed in each browser by the 4th execution.
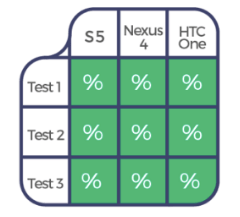
Here is another example applied to mobile testing in order to reduce risk related to device fragmentation.
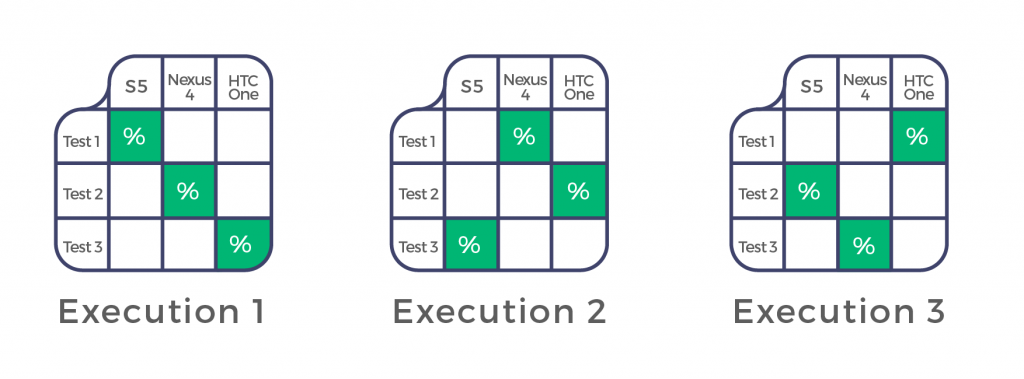

After the third execution, you’d have this coverage:
Conclusion
Test coverage criteria are very useful, but be careful with them because they do not guarantee anything. Some criteria are linked to others, when you forget one, you forget the rest and vice versa. We need to use the ones that best suit our needs and also consider priorities for each module and define coverage to look at each one according to priority and complexity. Finally, we can apply long-term coverage criteria to optimize test coverage over time.
Recommended for You
They Say Automation Increases Test Coverage, But What is Test Coverage Exactly?
The 4 Most Common Challenges in Test Automation (And How to Overcome Them)
Tags In


Federico Toledo, Chief Quality Officer at Abstracta
Related Posts
Automatic Checks with Scriptless Tool, Ghost Inspector
Ghost Inspector review: Tool to automate tests without the need for coding skills We just started a new project with a client from Silicon Valley in e-commerce where one of the first things we’re working on is to review their current testing strategy, and within that, their…
UI Testing Framework: A Blueprint for Building Your Own
Creating a robust UI Testing Framework is critical to building quality software. In this article, we delve into the nuances of developing an effective test automation framework, guiding you through the intricate landscape of UI testing. As businesses increasingly rely on software applications, the need…
Search
Contents
Categories
- Acceptance testing
- Accessibility Testing
- AI
- API Testing
- Development
- DevOps
- Fintech
- Functional Software Testing
- Healthtech
- Mobile Testing
- Observability Testing
- Partners
- Performance Testing
- Press
- Quallity Engineering
- Security Testing
- Software Quality
- Software Testing
- Test Automation
- Testing Strategy
- Testing Tools
- Work Culture