Discover the various types of performance testing and understand their key benefits. Learn about load, stress, throttle, peak, and scalability tests, and see how each one plays a vital role in boosting your systems to run smoothly and efficiently.


Performance testing is a type of non-functiona testing that evaluates how a system performs under conditions that impact the user experience. Understanding the various types of performance tests is essential for enhancing your applications to meet user expectations and perform reliably under diverse conditions.
This guide will help you make informed decisions to boost system efficiency, increase reliability, and deliver a consistent experience across all conditions.
Looking for a Performance Testing Partner? Explore our Performance Testing Services! Our global client reviews on Clutch speak for themselves.
Distinguishing the Different Types of Performance Testing


In our examination of performance testing types, we will explore load testing, endurance testing, stress testing, throttle testing, peak testing, spike testing, and scalability testing.
Every test of performance provides insights into metrics like response times, throughput, and resource utilization, based on carefully designed performance test scenarios. They also facilitate comparisons between different systems to determine which performs best and highlight necessary infrastructure and application enhancements.
By implementing the right performance testing environment, you can identify bottlenecks and make necessary infrastructure improvements across the software development life cycle.
Below, we share a figure that represents some of these performance tests and what the graph of active virtual users would be like throughout the testing time.
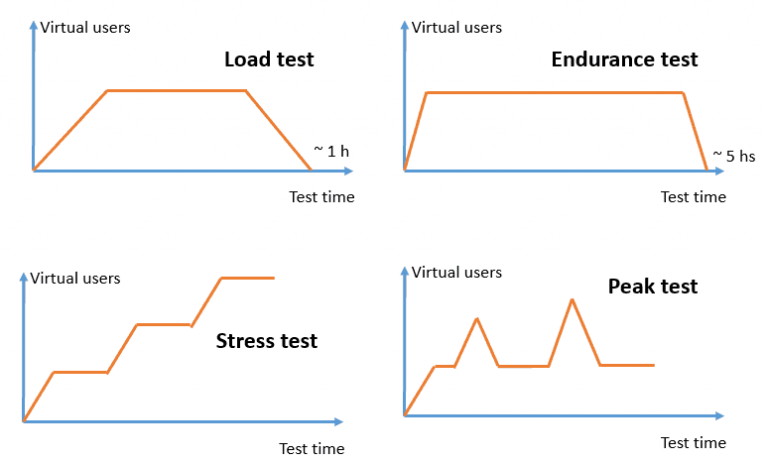

Now, let’s dive deeper into each type of performance test, starting with load tests.
Load Testing
Load testing simulates expected peak usage by evaluating system behavior with the projected number of concurrent virtual users and transactions over a defined time period.
For this, we must analyze the number of users (user traffic) that will have access and the operations that will be executed. When we hear our clients talking about the need to conduct performance testing before launching a product and also after shipping to production, most of the time they are referring to load testing.
There are many performance testing tools available in the market to execute a load test. You can find here our TOP Performance Testing Tools.
If you are looking for open-source software, a performance testing tool, or a free load testing tool, we recommend you to try JMeter DSL, an open-source project we support, focused on making performance testing developer-friendly.
Join us in this article to delve into the scope of API load testing.
Endurance Testing
Endurance testing, or soak testing, evaluates system performance during extended periods—typically 8 hours or more—to detect issues like memory leaks and gradual performance degradation.
Performed in a realistic environment, endurance testing verifies the system’s stability, reliability, and performance during continuous operation. It complements functional testing by focusing on long-term behavior, confirming the system remains operational and efficient during continuous operation.
By simulating long-term operations, these tests can reveal problems that might not be evident in shorter testing cycles, providing a more comprehensive assessment of system stability and performance.
Stress Testing
Stress testing pushes the system to its breaking point by gradually increasing the number of users running the most accessed transactions, typically until failure. It indicates the maximum number of users the system can support with the installed infrastructure, and how long it takes to recover normal operation after downtime.
We invite you to keep learning in this article: How to Stress Test a Website?
Throttle Testing
Throttle testing simulates user load with limited connection speed, applied to all virtual users or just a group. It measures response time in slow networks like 3G, distant areas, or the public internet. These tests use speed simulators, traffic shapers, or testing tools that include connection-throttling features.
Peak Testing
Peak testing analyzes how a system behaves when exposed to traffic peaks mixed with regular load, and observes recovery after the increased load. It evaluates performance under sustained high loads, like those caused by flash sales or viral events, nearing the system’s maximum load.
By conducting peak testing, you can identify potential bottlenecks, validate whether your system can handle high traffic volumes, and verify that it maintains performance without significant degradation.
Spike Testing
Spike testing evaluates system stability under sudden and extreme load increases or drops, compared to normal usage. It confirms the system can recover and stay functional.
This test is key to understanding how the system behaves during abrupt traffic changes, without crashing or showing severe performance degradation. It also helps verify stability under unpredictable conditions, revealing risks that don’t appear in regular test cycles.
Scalability Testing
Scalability testing examines how a system responds to increasing load and enables teams to analyze how the system scales as infrastructure or configurations change. Like other types of performance tests, it helps identify performance bottlenecks. It shows, for example, how many users are supported by adding a server, or how response times improve with more CPU on the database.
Running performance tests, including scalability tests, is crucial for understanding and enhancing the system’s ability to handle increased loads effectively.
If you are interested in learning more about the best continuous performance testing practices, we invite you to read this article.
Discover how we drive impact through performance testing—explore our case studies!
Beyond the Test Types: What Are You Measuring?
Besides knowing the different types of performance testing, it’s essential to understand what you aim to uncover with each test. So let’s take a look at the core criteria you should have in mind behind every performance test
The 3 Pillars of Effective Rigorous Performance Testing:
Understanding performance testing vs other QA approaches is key to building reliable systems. These three pillars define what truly matters when evaluating how well a system performs under real-world conditions.
Speed
Speed is the time a system takes to respond to user or system-triggered requests under expected load. It’s directly linked to response time and latency—two metrics that strongly influence user satisfaction. Choosing the right test depends on how speed affects your critical application flows.
Scalability
Scalability is the system’s ability to grow efficiently as user load or data volume increases. Unlike stress testing, which reveals breaking points, scalability testing analyzes sustainable performance as demands grow. It helps teams evaluate how well the system adapts during development.
Stability
Stability is the system’s ability to handle prolonged use or sudden changes without degrading performance. It includes monitoring memory usage, database performance, and long-term behavior in a production environment to detect early signs of risk.
While each of these pillars addresses a specific aspect of performance, they are tightly interconnected—stability under pressure often depends on both speed and scalability. They also help guide the selection and configuration of each type of performance test, and allow comparisons against defined performance benchmarks.
These criteria offer a practical framework for interpreting test results, identifying performance gaps, and making informed decisions about scaling infrastructure or enhancing system behavior within your development process.
The Bottom Line – Performance Tests


Understanding and implementing various types of performance testing is essential for empowering your applications to handle real-world conditions and deliver a seamless user experience. By proactively identifying and addressing performance issues, you can enhance system reliability, optimize resource utilization, and maintain high user satisfaction.
Moreover, performance testing supports informed decisions about infrastructure and helps validate improvements introduced across iterations. It allows you to simulate different scenarios, validating if your system can scale efficiently and recover gracefully from unexpected spikes in traffic.
Not only does this proactive approach save time and costs associated with post-launch fixes but also builds trust with your users by consistently delivering high performance. But can we really say that performance testing ensures system reliability? While nothing is guaranteed, performance testing significantly increases confidence in your system’s behavior under real conditions.
On top of that, this strategic investment in quality assurance ultimately leads to a more reliable product, higher user retention, and a stronger market position.
Want to keep on learning? Don’t miss our Continuous Performance Testing: A Comprehensive Guide!
FAQs – Different Performance Testing Types

What Is Performance Testing in QA?
Performance testing in QA evaluates how a software application performs under specific workloads. It measures speed, responsiveness, stability, and scalability to identify potential bottlenecks or areas where app performance might degrade. The goal is to enhance the user experience by fostering consistent performance under expected conditions.
What Is a Typical Performance Test?
A typical performance test simulates expected user activity under normal load. It measures response time, throughput, and resource usage to verify the system meets performance goals.
How Many Types of Performance Testing Are There?
There are several types of performance testing, each serving a specific purpose:
- Load Testing: Assesses the system’s behavior under expected user loads. Keep learning in this article.
- Stress Testing: Evaluates performance under extreme conditions or beyond normal capacity. Don’t miss this post to dive into this topic.
- Scalability Testing: Examines the system’s ability to grow as user demands increase.
- Endurance Testing: Verifies the system’s reliability over extended periods of use.
- Spike Testing: Analyzes the system’s response to sudden and significant traffic spikes.
- Volume Testing: Focuses on the system’s ability to handle large amounts of data effectively.
- Configuration Testing: Evaluates performance under different hardware and software configurations.
- Isolation Testing: Pinpoints performance issues by testing individual components or modules separately.
Note: Other types of performance testing might exist depending on specific industry practices or testing needs, such as latency testing or benchmarking. The types listed here represent the most commonly used categories in QA.
How Do Load, Stress, and Soak Testing Differ in Purpose and Approach?
Load testing checks performance under expected traffic, stress testing pushes the system to its limits, and soak testing reveals issues from extended, continuous use.
Which Performance Tests Are Best for Identifying Long-Term Stability Issues?
Endurance testing, also known as soak testing, is best for detecting long-term stability issues. It reveals problems like memory leaks or slow degradation during continuous system use.
What Tools Are Commonly Used for Executing Various Performance Tests?
Top tools include JMeter, JMeter DSL, k6, BlazeMeter, NeoLoad, Azure Load Testing, Gatling, OctoPerf, Locust, and LoadRunner. Each supports specific protocols, testing strategies, and integration needs. Check out our Top Performance Testing Tools for 2025.
What Are Common Performance Metrics?
Performance metrics are key indicators used to evaluate the effectiveness of performance testing. Common metrics include:
- Response Time: The time it takes for the system to respond to a user request.
- Throughput: The number of transactions or requests processed within a specific timeframe.
- Latency: The delay between a user’s action and the system’s response.
- Error Rate: The percentage of requests that fail during testing.
- CPU and Memory Utilization: The system resources consumed under different workloads.
- Concurrent Users: The number of users accessing the system simultaneously.
We recommend reading this article: Top 3 Performance Testing Metrics Explained.
What Is an Example of a Performance Test?
An example of a performance test is simulating a high volume of users logging into an e-commerce platform during a sale. This test observes the application’s response time, server stability, and overall performance under peak traffic conditions to identify opportunities for improvement.
Take a look at our performance testing case studies for more examples.
What’s the Difference Between Load Testing and Stress Testing?
Load testing checks how the system behaves under normal conditions or expected load, while stress testing pushes the system beyond its limits to uncover how it handles pressure. Unlike load testing, stress tests aim to reveal failure points, not just performance trends.
Why Is Test Data Important in Performance Testing?
Test data plays a critical role in the performance testing process. To measure performance accurately, the data used must resemble real-world scenarios. Incomplete or unrealistic datasets can lead to misleading test results.
What Role Does Capacity Testing Play in QA?
Capacity testing focuses on identifying the maximum amount of work a system can handle without performance degradation. It helps define infrastructure needs and supports decision-making during the development process.
What Are Popular Performance Testing Tools?
There are many tools available for executing performance tests. Some of the most popular performance testing tools include JMeter, JMeter DSL, k6, BlazeMeter, NeoLoad, Gatling, and LoadRunner. The right choice depends on your tech stack, goals, and desired level of automation.
Read this article to find out our top pick of performance testing tools, both open-source and proprietary.
How We Can Help You
With 17 years of experience and a global presence, Abstracta is a leading technology solutions company with offices in the United States, Chile, Colombia, and Uruguay. We specialize in AI-driven solutions and end-to-end software testing services.
We believe that actively bonding ties propels us further and helps us enhance our clients’ software. That’s why we’ve built robust partnerships with industry leaders, Microsoft, Datadog, Tricentis, Perforce BlazeMeter, and Saucelabs to provide the latest in cutting-edge technology.
We can help with conducting spike tests to assess how quickly a system can scale, recover, and handle sudden and extreme increases and decreases in load.
Our holistic approach enables us to support you across the entire software development life cycle.
Contact us! Unlock scalability and cost-effectiveness with our Performance Testing Services.

Follow us on Linkedin & X to be part of our community!
Recommended for You
How to Do Performance Testing for Web Applications?
DORA Metrics in DevOps
AI for Dummies, a Powerful Guide for All
Tags In


Sofía Palamarchuk, Co-CEO at Abstracta
Related Posts
A Quick BlazeMeter University Review
A senior performance tester’s review of the new courses by BlazeMeter Last week, I was looking for fresh knowledge on performance testing, so I asked a teammate of mine if she knew of any courses I could take. She recommended I try BlazeMeter University which…
How to Run Video Streaming Performance Tests with the HLS Plugin for JMeter
Using open source tools to stress test video streaming at scale In this post, I want to share something that we have been working on with BlazeMeter for several years. In this project, we had the opportunity to contribute to the open source code of…
Search
Contents
Categories
- Acceptance testing
- Accessibility Testing
- AI
- API Testing
- Development
- DevOps
- Fintech
- Functional Software Testing
- Healthtech
- Mobile Testing
- Observability Testing
- Partners
- Performance Testing
- Press
- Quallity Engineering
- Security Testing
- Software Quality
- Software Testing
- Test Automation
- Testing Strategy
- Testing Tools
- Work Culture





