Run every augmented reality test with purpose. Discover how AR QA boosts innovation across industries! See it in action: healthcare, finance, and beyond. Drive innovation hand-in-hand with Abstracta.


Have you ever wondered why augmented reality (AR) is so revolutionizing the way we interact with digital content? As strange as it may seem, AR technology is shifting how we see and engage with the world and, therefore, the manner in which businesses build connections with their audiences.
For instance, according to Statista, the mobile AR market hit an impressive $11.9 billion in 2024, and it’s not slowing down. By 2025, it’s projected to surge to $13.8 billion, signaling unstoppable growth in AR development.
By blending digital and physical spaces, AR creates new possibilities for everyday interactions. But it only works when it’s built with care. To stay ahead, businesses must embrace it with a focus on quality and rigorous testing.
The potential is huge—from improving efficiency to cutting costs across industries. The question is: Will you take the lead in leveraging AR’s power? Understanding its testing intricacies is crucial for delivering high-quality AR applications.
Now’s the moment to take action—let’s make it something truly meaningful.
Contact us for expert Augmented Reality Testing services!
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality Explained
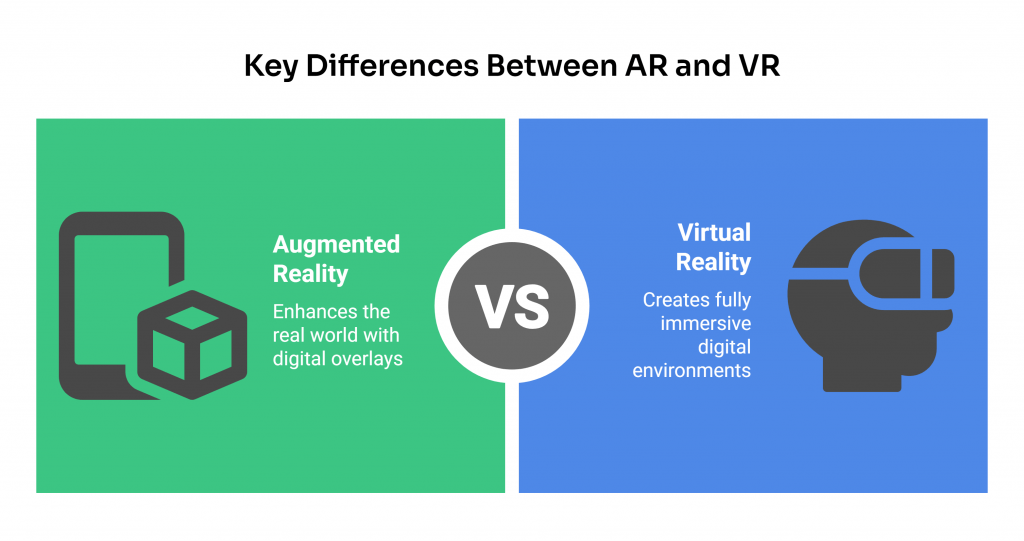

To fully grasp the importance of augmented reality testing (AR testing), it’s essential to differentiate between augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). These technologies, while related, serve distinct purposes and offer unique experiences.
AR overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing our perception of reality. In contrast, VR immerses users in a completely virtual environment, isolating them from the real world.
Key Differences Between AR and VR and Potential Applications
- AR enhances the real world with AR objects and virtual objects, providing users with an enriched experience that blends the physical and digital realms.
- AR Objects: These are digital objects that are integrated into the real-world environment. For example, in healthcare, AR can be used to overlay anatomical information onto a patient during surgery, providing surgeons with real-time data and improving precision.
- Virtual Objects: These are entirely digital constructs that can interact with the real world. In banking, AR can transform customer interactions by overlaying financial data and visualizations during consultations, making complex information more accessible.
- VR creates a fully immersive digital environment, isolating users from the real world.
- Immersive Experience: VR technologies provide a completely virtual experience, often used for simulations and training. For instance, VR can simulate surgical procedures for medical students, allowing them to practice in a risk-free environment.
- Isolation from Reality: Unlike AR, VR completely replaces the real world with a digital one, with virtual worlds. These can be beneficial for applications requiring full immersion such as gaming or virtual tours. In banking, VR can create virtual branches where customers can interact with financial advisors in a fully digital space using a VR headset.
- User Interaction: AR allows users to interact with both the real and digital worlds simultaneously, enabling seamless user experiences, whereas VR limits interactions to the virtual environment.
- AR Interaction: Users can manipulate AR objects in real-time, enhancing tasks like remote assistance or interactive learning.
- VR Interaction: Users interact within the virtual environment using controllers or motion sensors, which is ideal for activities like virtual reality gaming or virtual meetings.
- Applications: AR and VR have different use cases based on their unique capabilities.
- AR Applications: Common in fields like healthcare, retail, and education, where overlaying digital information in the real world can enhance understanding and decision-making.
- VR Applications: Widely used in gaming, training simulations, and virtual tours, where a fully immersive experience is required.
Understanding these differences is fundamental for developing and testing AR applications effectively. At Abstracta, we leverage our expertise to help your AR and VR applications deliver the best possible user experience.
See how we helped an AI startup unlock AR’s potential through shift-left testing. Read the case study here.
Common Types of Augmented Reality Tests


Testing augmented reality apps involves functional, accessibility, security, and performance testing, as well as evaluating user satisfaction. Each type of test addresses different aspects of the application, contributing to its overall quality, for both web and mobile apps.
Specifically, the augmented reality test focuses on how digital elements overlay and interact with the physical environment. By integrating the following types of tests, AR apps effectively overlay and interact with virtual objects while meeting essential standards.
This comprehensive approach blends digital and physical elements, resulting in high-quality AR experiences.
Types of Tests
- Functional Testing: This type of testing verifies that the application works as intended. As an illustration, in a healthcare AR app, functional testing would verify that anatomical overlays appear correctly and interact as expected with the real-world environment.
- Regression Testing: Verifies that existing functionalities continue to work as expected after code changes or updates. For example, it checks that previously stable overlays and interactions remain functional after new feature implementations.
- Performance Testing: This assesses the AR app’s responsiveness and stability. By way of example, it verifies that 3D objects render smoothly at 60 FPS, tracks objects accurately with low latency, and maintains performance under high device resource usage or varying network conditions.
- Compatibility Testing: Validates if the application performs well across different devices and operating systems. For instance, verifying that an AR app works seamlessly on both Android and iOS devices is critical.
- Security Testing: This safeguards user data and app functionality. Such as, it checks for secure data transmission (e.g., encrypted GPS and camera feeds), prevents AR marker spoofing, and ensures robust session authentication for multiplayer AR experiences.
- Accessibility Testing: Focuses on making the application usable for all users. Take or example, in a healthcare AR app, accessibility testing could evaluate features like text-to-speech functionality or high-contrast overlays to assist people with visual disabilities.
Looking for a software testing partner? Maximize your software quality and ROI through our Managed Testing Services!
Achieving Accuracy in AR Applications


Accuracy is paramount in AR applications to provide a realistic and reliable user experience. Achieving this level of precision requires a combination of advanced techniques and meticulous testing.
Techniques for Achieving Accuracy
Calibration
Regular calibration of sensors and cameras is essential to maintain accuracy. For instance, in a healthcare AR app, precise calibration enables anatomical overlays to align correctly with the patient’s body.
Algorithms
Advanced algorithms for precise tracking and overlay are crucial. In a banking app that utilizes augmented reality to help users locate nearby ATMs, these algorithms help to accurately interpret the user’s location and orientation, ensuring that the overlaid information aligns correctly with physical surroundings.
Testing Environments
Controlled environments to simulate real-world conditions are necessary. At Abstracta, we create comprehensive test environments that mimic various real-world scenarios, aiming for your AR applications to perform accurately in any setting.
In addition, we establish clear performance benchmarks to evaluate how the app behaves under realistic stress, latency, and rendering scenarios.
Challenges in AR Testing


Testing AR applications presents unique challenges that require a strong real-world testing process and innovative solutions. Addressing these challenges is essential for delivering high-quality AR applications.
Environmental Variability
Different lighting and physical conditions can affect the performance of AR applications. For example, a healthcare AR app used in a brightly lit operating room may perform differently than in a dimly lit patient room.
Solution: Implement adaptive algorithms that can adjust to varying lighting conditions and conduct testing in diverse environments. These actions help—but don’t always ensure consistent performance across all use cases, which is why continuous testing remains essential.
Potential Safety Hazard
Improperly tested AR applications can lead to risks for users, such as distractions while operating machinery or using AR while driving.
Solution: Incorporate rigorous safety protocols and real-world scenario testing to identify and mitigate potential hazards before deployment.
Hardware Limitations
Variability in device capabilities can impact the user experience. An AR app that works well on a high-end smartphone may not perform as expected on a lower-end device.
Solution: Optimize AR applications for multiple devices by conducting compatibility testing and hardware testing, promoting scalability of features based on device specifications.
User Interaction
Diverse behaviors from real users create variability in how users engage with AR applications. Different gestures, navigation methods, and responses to augmented elements can cause inconsistencies in user experience and application performance.
Solution: Conduct thorough user testing and implement adaptive design strategies to accommodate diverse interactions, providing a consistent and user-friendly AR experience.
Revolutionize Your Testing with Abstracta Copilot! Boost productivity by 30% with our new AI-powered assistant for efficient testing.
Security and Privacy in AR Applications


After addressing the various technical and user-centric challenges in AR application testing, we want to dedicate a whole section to security and privacy aspects, as we consider that protecting user data and maintaining trust is more important than ever.
Key Considerations
- Access Control: Implement robust authentication and authorization mechanisms to restrict access to sensitive data and functionalities within AR applications. This helps prevent unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
- Data Protection: Secure handling of user data is crucial. In healthcare, this means confirming that patient data is encrypted and protected at all times.
- Privacy Policies: Develop clear and transparent privacy policies to build trust with users. In general, this involves clearly communicating how customer data is used and protected.
- Security Testing: Conduct regular security assessments and updates to protect against potential threats. At Abstracta, we perform thorough security testing to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Incident Response Planning: Develop a clear plan for responding to security incidents. This includes procedures for detecting, reporting, and addressing security threats promptly to mitigate their impact.
- Compliance with Regulatory Standards: Adhere to relevant laws and industry regulations to protect user data and avoid legal repercussions. In healthcare, this involves complying with regulations such as HIPAA to safeguard patient information.
Having established the importance of security and privacy in AR applications, it is equally crucial to evaluate how these applications resonate with users.
Measuring User Experience in AR
User experience (UX) is a critical factor in the success of AR applications. It involves evaluating various metrics to help achieve a positive user experience.
Metrics for Measuring UX
- Engagement: User interaction and time spent on the app are key indicators of engagement. In healthcare, high engagement might indicate that medical professionals find the AR app useful and easy to use.
- Satisfaction: User feedback and ratings provide valuable insights into user satisfaction. In banking, positive feedback might indicate that customers find the AR app helpful for managing their finances.
- Usability: Ease of use and intuitive design are crucial for a positive user experience. In e-commerce, this means designing AR features that allow customers to effortlessly visualize products in their own environment, enhancing their shopping experience and increasing the likelihood of purchase.
- Task Success Rate: Measures how effectively users can complete specific tasks within the AR application. In the tech industry, IT professionals using an AR tool to diagnose network issues achieve a high task success rate when they can quickly identify and resolve problems without additional assistance.
- Error Rate: Tracks the frequency of user errors while interacting with the AR application. In healthcare, a low error rate occurs when nurses accurately input patient information into an AR system, minimizing the risk of medical inaccuracies and enhancing patient care.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Gauges user willingness to recommend the AR application to others. In retail, a high NPS is seen when customers enthusiastically share their positive experiences with an AR shopping app, indicating strong satisfaction and loyalty
- Retention Rate: Monitors the percentage of users who continue to use the AR application over time. In finance, a high retention rate occurs when investors regularly access an AR platform to monitor their portfolios, demonstrating that the application consistently delivers valuable insights.
- Accessibility: Evaluates how people with disabilities navigate and utilize the AR application. In retail, designing AR features with voice commands and adjustable text sizes allows customers with visual disabilities to interact seamlessly, expanding your customer base and boosting overall satisfaction.
Future Trends in Augmented Reality


The future of AR is promising, with several trends set to shape the industry. Staying ahead of these trends is essential for delivering cutting-edge AR applications.
5G Integration
The deployment of 5G technology continues to revolutionize AR experiences by providing faster speeds and lower latency. This advancement enables more complex and data-intensive AR applications, such as real-time remote consultations in healthcare and seamless AR shopping experiences in e-commerce.
AI and Machine Learning
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning enhances interactivity and personalization in AR. These technologies support more adaptive AR experiences, including customized training programs in healthcare and personalized financial advice in banking. Future AI-driven AR applications will become more intuitive, anticipating user needs and providing smarter, context-aware interactions.
Wearable Technology
Advancements in wearable AR devices, such as smart glasses, are making them more immersive and portable. Future developments will focus on improving battery life, comfort, and seamless integration with other devices. These improvements open new possibilities for complex surgeries with augmented overlays, telemedicine consultations, and immersive product demonstrations in e-commerce.
Spatial Computing
Spatial computing combines AR with advanced sensors and environmental understanding, allowing AR applications to interact more naturally with the physical world. This trend enables seamless integration of virtual and real objects, leading to sophisticated virtual workspaces, enhanced collaborative tools, and more immersive gaming and educational experiences.
Haptic Feedback
Incorporating haptic feedback into AR experiences revolutionizes user interaction by providing tactile sensations that correspond to virtual elements. This enhances the realism of AR applications, making interactions more intuitive and engaging.
Edge Computing
Edge computing processes data closer to the user, reducing latency and improving AR application performance. This trend facilitates more responsive and reliable AR experiences, particularly in environments where real-time processing is critical, such as industrial maintenance, healthcare diagnostics, and interactive retail experiences.
Extended Reality (XR) Convergence
The convergence of AR with virtual reality (VR) and mixed reality (MR) under the umbrella of extended reality (XR) paves the way for more versatile and comprehensive immersive experiences. Future AR applications will leverage the strengths of XR to offer dynamic and flexible solutions.
Wrapping Up: The Road Ahead for AR Testing
The field of augmented reality is rapidly evolving, and staying ahead requires continuous learning and adaptation. By understanding augmented reality test types, their challenges, security measures, metrics, and future trends, we can help deliver high-quality AR applications through evolving testing practices.
FAQs about Augmented Reality Testing

How to Test Augmented Reality?
Testing augmented reality involves functional, performance, and usability testing, using tools like ARKit, ARCore, and Vuforia.
What are The 3 Types of Augmented Reality?
The three types of augmented reality are marker-based AR, markerless AR, and location-based AR.
Marker-based AR utilizes specific images or patterns, known as markers, that the device’s camera recognizes to trigger and overlay digital content onto the real-world environment.
Markerless AR does not require physical markers. Instead, it relies on sensors and technologies like surface recognition or geolocation to position digital content dynamically within the user’s space.
Location-based AR leverages the user’s geographic location to deliver relevant information or digital enhancements based on where they are.
(Note: Location-based AR is sometimes considered a subcategory of markerless AR due to its reliance on geolocation rather than physical markers.)
Is Oculus a VR or AR?
Oculus is primarily a VR (virtual reality) platform, providing immersive virtual experiences.
How We Can Help You

With over 16 years of experience and a global presence, Abstracta is a leading technology solutions company with offices in the United States, Chile, Colombia, and Uruguay. We specialize in software development, AI-driven innovations & copilots, and end-to-end software testing services.
Our expertise spans across industries. We believe that actively bonding ties propels us further. That’s why we’ve forged robust partnerships with industry leaders like Microsoft, Datadog, Tricentis, Perforce, and Saucelabs, empowering us to incorporate cutting-edge technologies.
Our holistic approach enables us to support you across the entire software development life cycle.
Visit our solutions page and partner with us for unmatched augmented reality testing solutions!

Follow us on Linkedin & X to be part of our community!
Recommended for You
UX Writing: Crafting Impactful Content for Memorable Experiences
Tags In


Abstracta Team
Related Posts
Static Testing vs Dynamic Testing: A Mindset-First Shift
Static testing vs dynamic testing seen through Abstracta’s mindset-first approach, where early review and predictive signals shape quality from the start.
Co-Development Software for Enterprise Impact
Abstracta turns silos into synergy. With co-development software powered by AI agents and strong partnerships, teams deliver measurable business outcomes.
Search
Contents
Categories
- Acceptance testing
- Accessibility Testing
- AI
- API Testing
- Development
- DevOps
- Fintech
- Functional Software Testing
- Healthtech
- Mobile Testing
- Observability Testing
- Partners
- Performance Testing
- Press
- Quallity Engineering
- Security Testing
- Software Quality
- Software Testing
- Test Automation
- Testing Strategy
- Testing Tools
- Work Culture





