

The world is on the brink of a fundamental shift in how financial data is accessed, shared, and protected. As countries prepare to implement their long-awaited open banking framework, financial institutions, fintech companies, and service providers must adapt quickly.
From Europe’s unified implementation to Canada’s regulatory momentum and the United States’ fragmented but growing landscape, organizations worldwide are looking to smoothly transition toward a more connected, customer-centric financial landscape.
At the core of this transformation lie banking APIs—but the real opportunity goes further. These standardized interfaces will replace outdated methods like screen scraping, unlocking safer and more efficient ways for third-party providers to deliver value-added services to banking customers—without compromising security or control.
Furthermore, the rise of AI agents is unlocking new ways to interpret open banking data, automate decision-making, and enhance the customer experience in real time. Combined with robust API infrastructures, these agents are driving smarter, faster, and more scalable solutions.
At Abstracta, we help companies build intelligent, secure, and high-performing open banking ecosystems. From API testing to custom AI agent development, we’re ready to help you lead this transformation.
Looking to validate your open banking APIs? We can help you get there faster and safer.
Let’s talk!
Understanding Open Banking
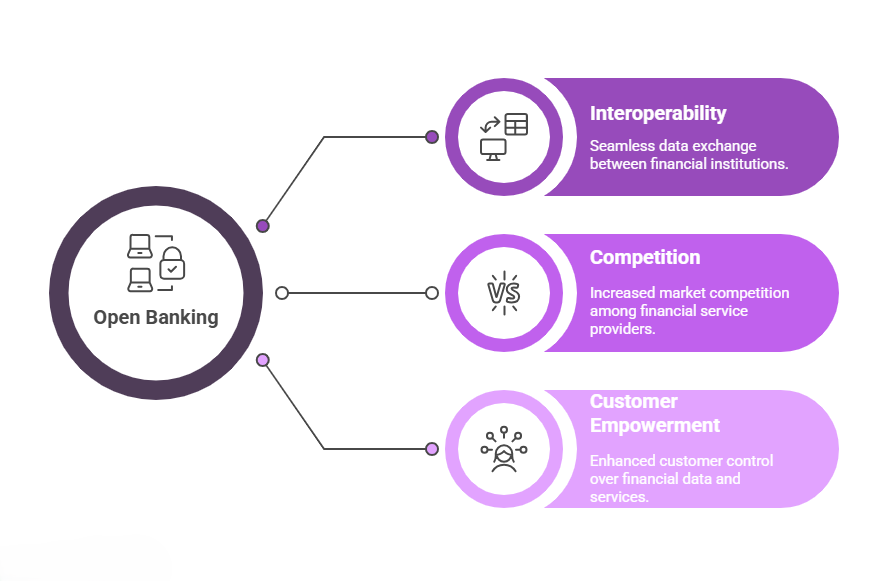

Open banking, sometimes referred to as consumer-driven banking, is a system that allows individuals and businesses to share their financial data securely with authorized third parties. Through open banking APIs and with user consent, they can share data across multiple bank accounts and financial institutions consistently and securely.
Unlike traditional banking services, where financial information remains siloed within a customer’s bank account, open banking promotes interoperability and competition. It also empowers customers to choose financial services that best suit their needs, such as budgeting tools, personalized financial products, and consolidated money management apps.
How Open Banking APIs Work


Open banking APIs serve as the technical infrastructure that enables secure, real-time data sharing between banks and authorized third parties. These APIs allow for controlled access to account information, transaction data, and other financial records, replacing older, less secure methods.
This shift is not just technological—it’s structural. It changes how customer data is handled, how financial applications interact with banking systems, and how new services are delivered to the market.
Here’s a simplified view of the differences:
| Traditional Data Sharing | Open Banking API Model |
|---|---|
| Screen scraping | Standardized, secure APIs |
| Requires sharing login creds | Uses token-based authentication |
| Difficult to regulate | Governed by open banking regulation |
| Limited user control | Granular, consent-based access |
| Fragile and error-prone | Reliable and interoperable |
The Benefits of Open Banking
The benefits of open banking span across consumers, financial institutions, and the broader financial services industry.
For Consumers
Open banking empowers users to access financial data from various accounts in one place. It enables smoother onboarding for financial products, easier demonstration of creditworthiness, and real-time visibility into personal finances. By connecting securely with financial apps, users can manage subscriptions, plan savings, and automate money management tasks—all while maintaining control over their data.
It also reduces exposure to risk by eliminating the need to share banking credentials, lowering the chances of fraud and unauthorized access.
For financial Institutions
Banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions can use open banking to unlock new business models and revenue streams. Rather than competing with fintech companies, they can collaborate to offer innovative financial services built on top of trusted infrastructure.
Open banking also increases operational efficiency by reducing integration costs, improving data accuracy, and enabling faster innovation cycles through banking as a service. It supports the development of scalable APIs that meet both user expectations and regulatory requirements.
Explore our AI Development & Agents Services!
A Global Market Opportunity


Open banking is not only a regulatory change—it’s a global opportunity. As different regions move at varying speeds, understanding the worldwide landscape is key to building scalable, forward-thinking strategies.
Europe: The Forerunner
The European Union has led the way in open banking implementation. Under the PSD2 regulation, open banking has been fully deployed across all member states for over three years. It is now a standard part of the financial services ecosystem, enabling cross-border data portability and mobility for consumers. The regulation enables a unified market, creating an environment ripe for innovation and seamless financial experiences.
Canada: Leading in The Americas
Canada is the most advanced country in the Americas when it comes to open banking readiness. While the government initially targeted implementation by 2022, the timeline shifted due to policy coordination, stakeholder alignment, and prioritization delays caused by the pandemic and evolving global trade pressures.
Although still in its pre-implementation phase, Canada’s adoption of open banking is advancing. The federal budget of April 2024 included funding to complete policy development. The framework is expected to be finalized in 2025, with theoretical implementation by 2026. This creates a limited but critical window for stakeholders to prepare, test, and align their systems with the upcoming model.
The Retail Payment Activities Act strengthens the supervision of payment service providers, while Bill C-27 will define how personal and customer data is managed and protected across digital ecosystems.
However, the impact of U.S. tariff policy and cross-border considerations may influence this trajectory.
United States: Complex and Fragmented
The U.S. is behind Canada in implementing open banking due to its complex system of federal and state-level regulation. While some states—like California—are pushing for local frameworks and have suggested rollout as early as 2025, these remain unconfirmed and speculative.
Meanwhile, federal authorities continue to debate and draft legislation without clear timelines. Some banks and fintechs have started building systems in anticipation, but the lack of a centralized regulatory roadmap poses challenges for nationwide adoption. It is estimated that financial institutions need at least 8–12 months of lead time once regulations are finalized.
Latin America: Fragmented and Nascent
Latin America presents a highly diverse and uneven landscape. While Brazil is advancing through its phased implementation of open banking and open finance, most other countries are in the very early stages or have not included open banking in their financial reform agendas.
Countries like Mexico and Colombia have begun preliminary discussions or introduced related fintech laws, but widespread implementation remains distant. For many markets in the region, regulatory clarity and infrastructural investment are still lacking.
Asia: Rapid, Varied Progress
Asia reflects a spectrum of approaches. Countries like Singapore and South Korea have taken proactive steps, fostering government-backed frameworks and clear API standards. Singapore’s Monetary Authority has supported data-sharing initiatives since 2016.
In contrast, markets like India are advancing open finance under broader initiatives such as IndiaStack and the Account Aggregator framework. Meanwhile, countries such as Japan and China are experimenting with data-sharing models, but progress varies by market maturity and regulatory philosophy.
Use Cases: What Open Banking Enables
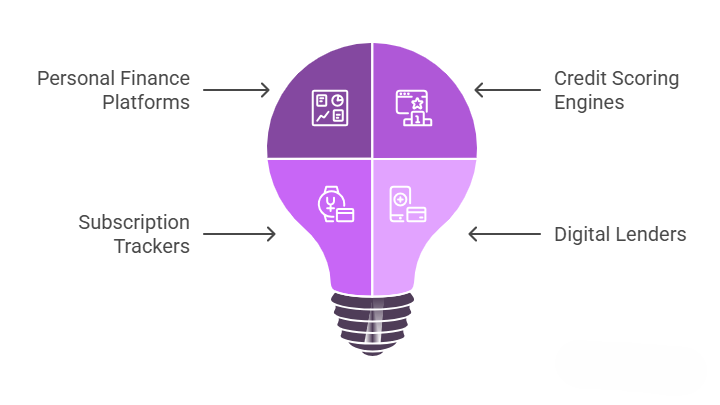

Open banking enables a wide range of new services that weren’t previously possible—or practical—with traditional financial services. Here are a few examples:
- Personal finance platforms that integrate financial accounts from different banks to provide a unified dashboard and actionable insights.
- Credit scoring engines that leverage verified transaction history and account balances to offer fairer, real-time assessments.
- Subscription trackers and budgeting tools that help users understand and control their spending habits.
- Digital lenders that instantly access relevant financial data to speed up approvals and reduce paperwork.
These new services not only benefit users but also push the banking industry to modernize and compete more effectively.
Why Software Testing Matters Now


As open banking rolls out, having well-tested, secure, and high-performing banking APIs becomes a competitive differentiator. Poor implementation can lead to system instability, security vulnerabilities, and compliance failures.
Testing these APIs must go beyond functional validation. It requires a rigorous performance testing process that includes:
- Validation of how the system performs under expected load
- Security testing to detect vulnerabilities in customer-facing endpoints
- Regression testing across multiple banking products and customer journeys
- Test automation to ensure continuous validation across environments
With different providers interacting through APIs, every piece of the system must be verified to avoid integration failures and protect customer data.
AI Agents in Open Banking: Turning APIs Into Smart, Scalable Solutions
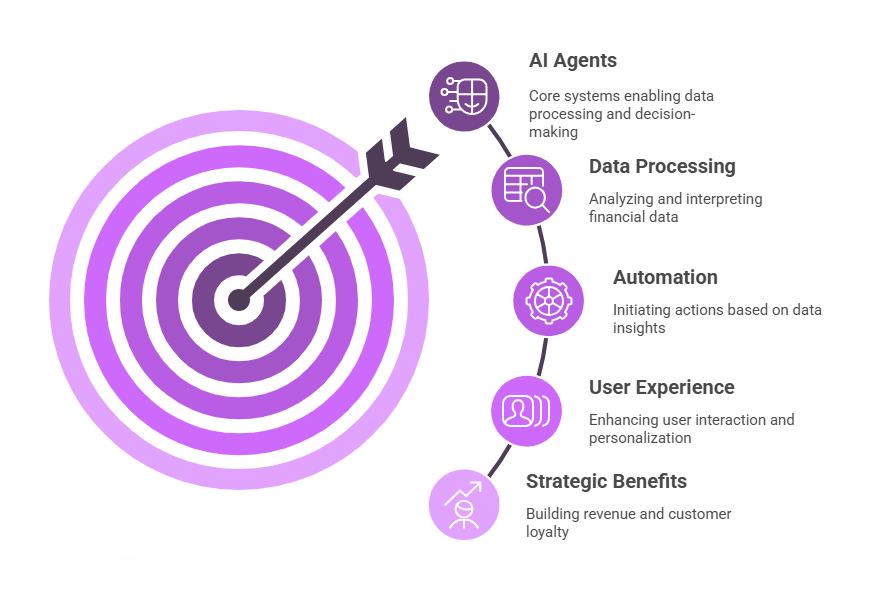

As open banking matures, API availability alone is no longer enough. The real value lies in what financial institutions and third-party applications can do with that data, and AI agents are key to unlocking it.
AI agents are intelligent systems that operate autonomously to process data, make decisions, and trigger actions. In open banking, they can:
- Monitor and interpret cash flow and spending behavior in real time
- Initiate payments or alerts based on pre-set conditions
- Analyze open banking data across multiple accounts and institutions
- Help users manage finances with proactive, personalized recommendations
- Connect with accounting software or financial apps to optimize workflows
- Reduce operational risk by flagging anomalies, fraud, or regulatory issues
By combining financial APIs with intelligent automation, AI agents transform raw account data into actionable insights. This elevates both user experience and operational efficiency across the entire open banking model.
Organizations that integrate AI agents early can build new revenue streams, strengthen customer relationships, and offer products and services that evolve as fast as their users do.
FAQs about Open Banking


What Is the Concept of Open Banking?
Open banking is a financial model that allows individuals and businesses to securely share data from their user bank accounts with third-party service providers using application programming interfaces. With consumer-permissioned data, users authorize other platforms to access their account data, initiate payments, and process transactions on their behalf. This fosters transparency, competition, and innovation in consumer banking by enabling a broad range of financial products and services built around real-time access.
What Are APIs in Open Banking?
APIs (application programming interfaces) are standardized tools that enable secure communication between financial institutions and third-party applications. These interfaces provide controlled access to account data, including balances and transaction history, allowing other third parties to build solutions that enhance customer experience and streamline financial services.
What Is a Simple Example or Use of Open Banking?
A budgeting app that connects to savings accounts from other banks and aggregates financial information into a single dashboard is a simple example of open banking. These platforms, known as account aggregation services, help users manage their money and improve consumer access to real-time account data.
What Is an Example of a Bank API?
An example would be a bank API that lets a FinTech app retrieve account balances and transaction history from a user’s bank account. These API connections power integrations with accounting software, track cash flow, and help process transactions efficiently, improving both compliance and customer relationships.
What Is the Difference Between OpenAPI and Open Banking?
OpenAPI is a standard for describing how APIs work. Open banking, meanwhile, is a regulatory and business model where financial institutions expose APIs to eligible third parties—often documented using OpenAPI—to allow users to share data securely. The OpenAPI standard helps unify the data format and ensure interoperability across the financial sectors.
What Is the Difference Between Open Banking and Normal Banking?
Normal banking involves using only a single institution’s services, typically through online banking. Open banking, by contrast, allows users to share data across institutions with authorized third parties, enabling integration with external platforms and unlocking broader service offerings and greater financial visibility.
Is Open Banking Allowed in Canada?
Canada is developing a national open banking framework. While there is no confirmed implementation date, regulatory foundations are in place. The system will be supervised by a designated market authority and designed to promote consumer access and new revenue streams for financial institutions.
What Does Open Banking Mean in Canada?
In Canada, open banking means empowering consumers to safely share their financial information with third-party service providers. The goal is to foster innovation, enable secure data sharing, and support the modernization of consumer banking while protecting against security risks and data breaches.
Is Open Banking Legal in the US?
Open banking is not yet federally regulated in the United States. Regulatory progress is slowed by differences between federal and state systems. Some states, such as California, are leading local initiatives, while others lag behind. Tech companies and financial institutions are preparing regardless, anticipating future regulation and building early API traffic models.
What Is the Rule 1033 for Open Banking?
Rule 1033 is a proposed U.S. regulation from the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB). It would require financial institutions to provide consumers with access to their own account data, enabling them to share it with third-party applications. While not yet implemented, it could form the backbone of a future open banking model in the U.S.
What Are the Risks of Open Banking?
Open banking introduces risks such as unauthorized access, misuse of consumer data, or data breaches. These are mitigated through secure authentication protocols, clear user consent mechanisms, and strict oversight of financial APIs. Institutions must ensure that only trusted third parties gain access to sensitive data.
Is Open Banking a Good Idea?
Yes—open banking offers significant benefits. It improves customer experience, promotes competition, and enables innovation through seamless API connections. It also allows banks and third-party service providers to deliver more relevant, personalized products and services while supporting stronger customer relationships.
How Abstracta Supports Financial Services Teams

With over 16 years of experience and a global presence, Abstracta is a leading technology solutions company with offices in the United States, Chile, Colombia, and Uruguay. We specialize in software development, AI-driven innovations & copilots, and end-to-end software testing services.
At Abstracta, we help companies in the financial services industry build reliable, secure, and scalable API ecosystems. Whether you need to test mission-critical integrations or build intelligent digital experiences from the ground up, our team is ready to support you.
Our services include:
- End-to-end API testing for open banking implementations
- Performance testing of banking APIs under real-world conditions
- Security and compliance testing aligned with emerging regulations
- Automation frameworks tailored to your banking products and development process
- Custom development of financial software and platform components
- AI agent development and integration, using open banking data to deliver smarter, context-aware user experiences
- Product ideation and co-creation, turning your vision into fully functional solutions
From banks and credit unions to fintech startups and third-party service providers, we partner with organizations ready to lead the future of financial technology.
We believe that actively bonding ties propels us further and helps us enhance our clients’ software. That’s why we’ve built robust partnerships with industry leaders Microsoft, Datadog, Tricentis, Perforce BlazeMeter, and Saucelabs to provide the latest in cutting-edge technology.
Our holistic approach enables us to support you across the entire software development lifecycle.
At Abstracta, we help forward-thinking teams turn open banking into a competitive advantage. Contact us to enhance your software quality!

Follow us on LinkedIn & X to be part of our community!
Recommended for You
QA Outsourcing vs In-House Team: What’s The Smarter Move?
JMeter API Testing: How to Automate API Performance Tests
Why SRE? The Essential Role of Site Reliability Engineering
Natalie Rodgers, Content Manager at Abstracta
Related Posts
Data Strategy in Financial Services: From Compliance to Reliable Decision-Making
Most strategies in finance fall short. This guide shows how to build a data strategy that supports AI, strengthens compliance, and creates measurable business value. A data strategy in financial services defines how institutions turn raw data into reliable, traceable insights. It aligns governance with…
AI SaaS Product Classification Criteria for Banking and Fintech
AI SaaS product classification criteria. A practical framework focused on governance, compliance, and enterprise decision-making for banking and fintechs.
Search
Contents
Categories
- Acceptance testing
- Accessibility Testing
- AI
- API Testing
- Development
- DevOps
- Fintech
- Functional Software Testing
- Healthtech
- Mobile Testing
- Observability Testing
- Partners
- Performance Testing
- Press
- Quallity Engineering
- Security Testing
- Software Quality
- Software Testing
- Test Automation
- Testing Strategy
- Testing Tools
- Work Culture





