Shift-left testing goes far beyond theory. Prevent costly defects early and strengthen your strategy by pairing it with shift-right for sustainable growth.


Fixing a bug in production can cost 100x more than catching it early. We know by experience that’s not just theory, it’s the hidden tax slowing down many companies’ growth. That’s why we advocate for rethinking the software development lifecycle and implementing shift left from the very beginning
With Agile practices and continuous monitoring becoming a norm, early testing has emerged as a powerful way to build reliable, scalable software. It’s how testing stops being a final check and becomes a continuous presence throughout the software development process. This perspective positions quality as a driver of sustainable growth, not just as a short-term safeguard.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the key concepts and benefits of shift left software testing, and how to approach it effectively. We’ll also explore how combining it with shift-right testing can enhance your strategy and overall software quality.
Want to move from theory to impact?
Explore our solutions webpage and see worldwide case studies in action!
What is The Shift-left Testing Approach?


The shift-left testing approach involves moving testing activities to the earlier stages of the software development cycle, where testing starts early to reduce risks and rework. Instead of waiting until the end to test, shift left focuses on enabling development and testing teams to collaborate from the start to identify and fix issues as early as possible. This improves software quality and reduces costs and development time.
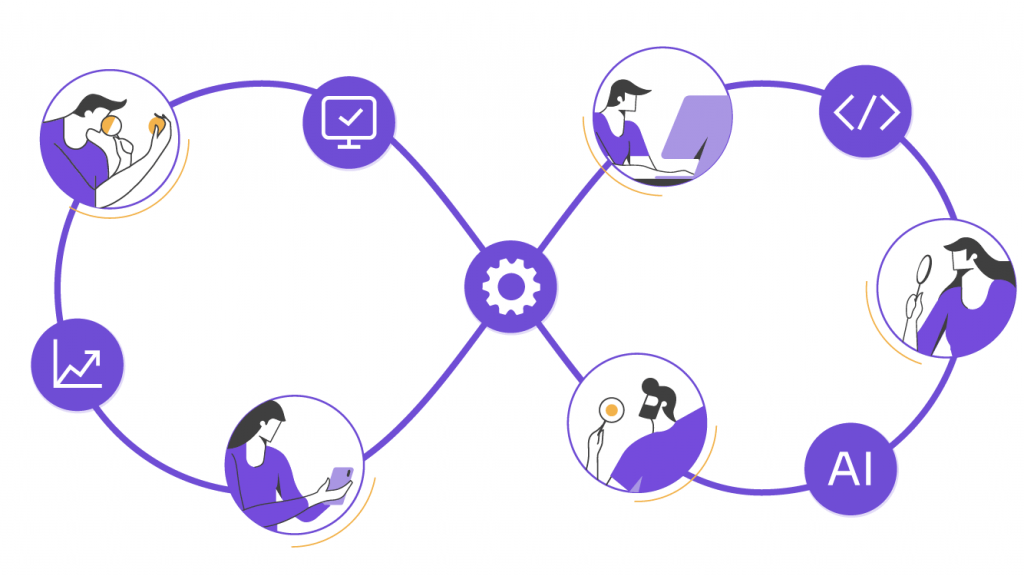
To truly excel and advance today, a tester must not only be great at testing but also be an engineer of the agile testing process. This means working together with development and operations teams and analyzing quality during every stage of development, as shown in the graphic below.
For instance, testers have to jump in and take a more proactive role even before development starts by being present during the gathering of testing requirements.
Benefits of Shift Left Testing: Why It Matters for Your Business
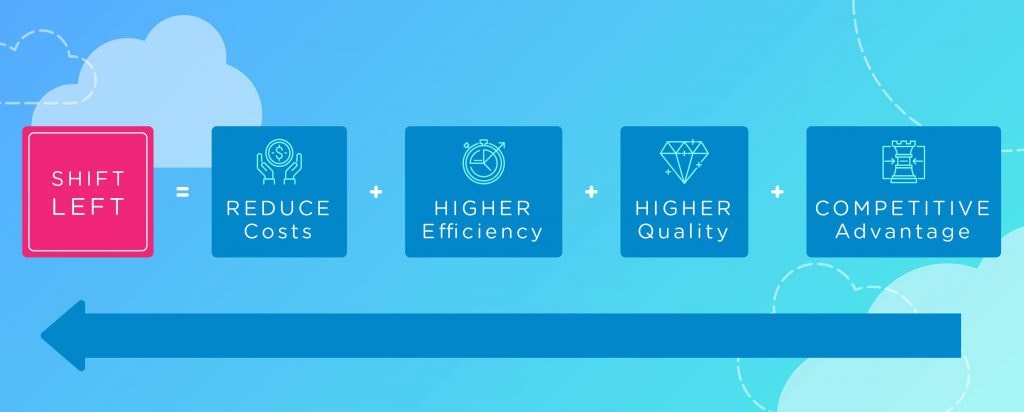

Shift left testing delivers measurable outcomes, making the shift left approach a strategic investment in software quality and long-term growth. Here’s a breakdown of the benefits of shift left testing:
1. Reduced costs
It is still true what Larry Smith said over 20 years ago when the “shift-left” concept was first introduced: “Bugs are cheap when caught young.”
One of the aims of Agile testing is early bug detection, to identify errors as soon as possible. What we mean by as soon as possible is: as soon after the exact moment in which the error was inserted into the system.
When you test with every build (especially during unit testing), you may find smaller errors that are easier to detect, locate, and fix at a lower cost. Maintaining quality as you go also leads to cost savings by mitigating the tremendous costs and unnecessary work of going back and redoing certain things.
Business benefits: Significant cost savings across the software development lifecycle, avoiding the hidden tax of late rework.
Want to know how much money you can save with test automation? Check out this post on the ROI of test automation.
2. Increasing Efficiency & Quality
We often find that the increased levels of automation when shifting left allow for better test coverage, as well as:
- Increasing test coverage by running more tests in the same amount of time
- Freeing up time for testers to focus on more challenging and rewarding tasks
- Reducing human error
- Monitoring performance over time
- Code quality checks
- Built-in security checks
- Reducing issues in production (that users will face)
Beyond these benefits, being able to start testing sooner invariably results in more quality, as testers are no longer rushing to find all the errors at the end. This requires adopting a shift left mindset, where quality is owned collectively and considered from day one.
Business benefits: Apart from improving the testing process, this efficiency frees up development and operations teams to focus on innovation, strengthening overall software quality.
3. Gaining a Competitive Edge
Shifting left your QA gives you a competitive edge in two ways: you can speed up time to market and attract top talent.
About staying competitive in today’s ever-changing technological landscape, Alon Girmonsky, founder of BlazeMeter, said it best:
“Today, the barrier to compete is minimal, and the only way to defend one’s stature is by innovating in short iterations… meaning adopting Agile.” – Alon Girmonsky
As we can all agree that it is important to deliver software more quickly, it also shouldn’t be rushed out the door. Shift-left testing answers the problem of accelerating development without sacrificing quality, leading to higher customer satisfaction with each release.
Business benefits: The result is faster, consistent releases that exceed customer expectations, strengthen quality assurance, and build a stronger position in highly competitive markets.
4. Accelerating Time to Market
The pressure to release faster is real, but doing so without the necessary checks often leads to setbacks that cost more than a delayed sprint. Shift-left testing helps teams move quickly without sacrificing stability.
By catching defects early, validating assumptions sooner, and integrating quality from the start, teams can deliver functionality with fewer surprises and less rework, minimizing late-stage bottlenecks.
Business benefits: This acceleration across the development cycle allows organizations to capture market opportunities earlier and maximize ROI from each release.
5. Encouraging Stronger Collaboration
One of the most meaningful shifts doesn’t come from new tools but from new conversations. When quality is part of the conversation from day one, QA, Dev, and Product stop working in isolation and start co-creating.
This leads to sharper definitions, fewer misunderstandings, and stronger outcomes. Shift-left testing invites QA to help shape the work, not just validate it. And when collaboration starts earlier, the entire development process becomes smoother, more thoughtful, and more aligned with user needs.
Business benefits: Early collaboration across testing and development teams also reduces friction and creates a culture of continuous improvement.
6. Identifying Risks Sooner
The later you discover a critical issue, the harder it is to solve. Shift-left testing allows teams to identify risks before they escalate, from code vulnerabilities to performance bottlenecks to misaligned expectations.
By integrating testing into early design and planning stages, you gain visibility into what might go wrong while you still have time to course-correct. This helps build confidence across the team, making releases less stressful and more predictable.
Business benefits: Early risk visibility limits financial exposure, protects brand reputation, and allows organizations to plan releases with greater certainty.
Key Activities for Testers in Shift-left Testing
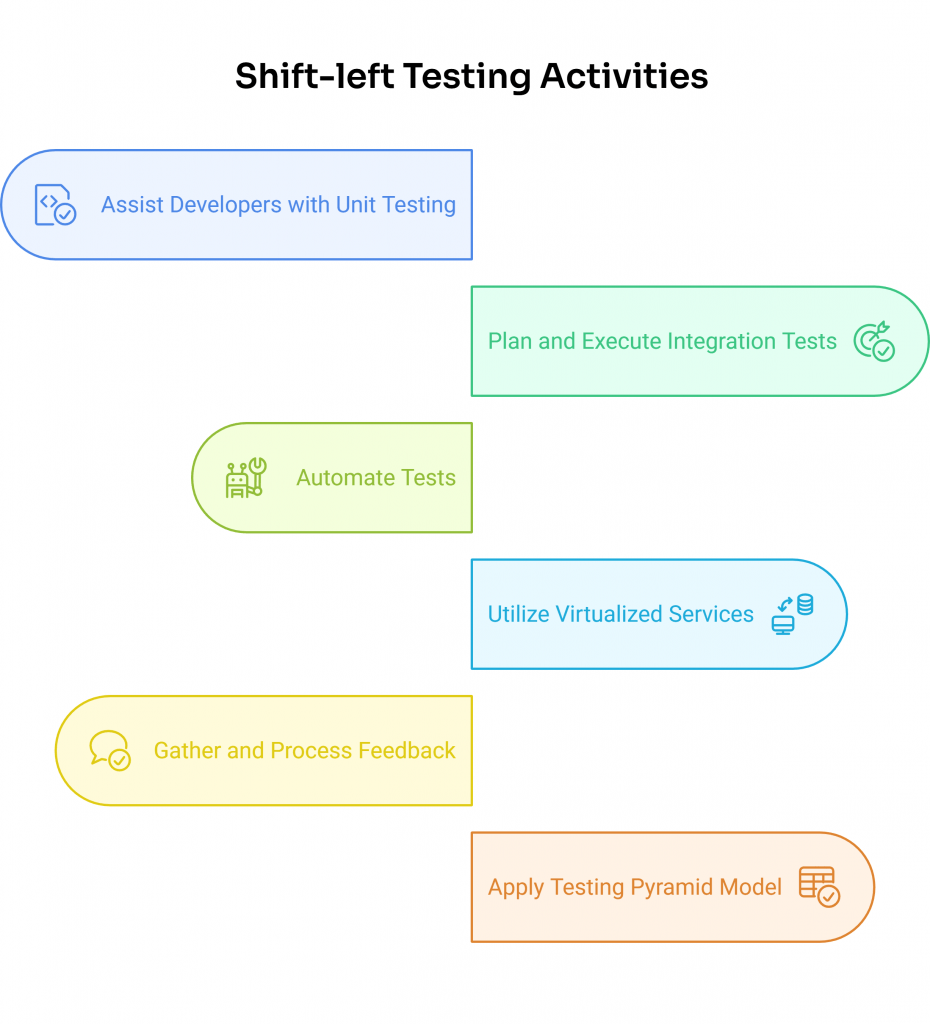

Here are some of the crucial tasks testers take on in a shift-left approach:
- Helping developers implement unit testing: Testers collaborate with developers to create and run unit tests, verifying that individual components work correctly from the get-go.
- Planning, creating, and executing integration test cases: Testers focus on writing test cases and executing them to check how different parts of the system interact, catching issues early in the integration phase.
- Automating tests: Testers deploy automated tests to make the testing process faster and more reliable. By integrating automated unit tests as part of this approach, as well as API and UI testing where necessary, they can achieve greater coverage and identify issues earlier within the development workflow.
- Employing virtualized services at every stage and component level: By using virtualized services at every stage and component level, testers can simulate different parts of the system, making it easier to test components in isolation and in various scenarios.
- Gathering, prioritizing, and processing feedback: Testers collect feedback from various stages of development, prioritize it based on impact, and address it promptly. This contributes to a loop of continuous feedback that helps guide product quality throughout the lifecycle.
- Applying the testing pyramid model: Structure your test suite with a broad base of automated unit tests, a smaller set of integration tests, and a minimal layer of end-to-end tests. This distribution promotes faster feedback cycles and greater test stability as teams shift left.
Process Changes During the Shift
Shifting left also brings about some significant process changes:
- Frequent code integration: Rather than waiting weeks to add code to that of the rest of the team, integrate code changes every day, or even several times a day, to catch issues early.
- Continuous quality analysis: Instead of detecting problems at the end, continuously analyze quality as development progresses to address issues early and maintain steady product quality.
- Considering a static code analyzer: While not mandatory, using these tools can be helpful to detect vulnerabilities, syntax issues, and logic flaws early in development, without executing the code. It’s a valuable addition to dynamic testing efforts and can enhance code quality when applied appropriately.
- Integrating security scanning tools: Tools like Static Application Security Testing (SAST) and Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) can help identify vulnerabilities early in the pipeline. While not required in every context, they’re a valuable option for embedding security checks into the development cycle.
- Early involvement of testers: Get testers involved from the very beginning, even during the requirements gathering phase, to identify potential issues early.
- Collaborative development: Foster a culture of collaboration between developers, testers, and operations and make quality a shared responsibility throughout the development process.
Revolutionize Your Testing with our AI-powered assistant Abstracta Copilot!
Book a meeting and talk with our experts about how we can support you.
When Shift-Left Testing Doesn’t Work


Maybe you have already heard all of those benefits, but you are STILL not convinced about shift-left testing for this reason: you’ve seen that even Agile teams can face the same bottlenecks as seen in Waterfall.
For example, as Shridhar Mittal, former GM of Application Delivery at CA Technologies, explains, “Due to the complexity of environments and composite applications, Agile teams are often stuck waiting in a queue once all of the pieces come together in the performance and user acceptance testing phases.”
The solution he provides that we agree with is utilizing service virtualization. Service virtualization emulates the behavior of essential components that will be present in production, enabling integration tests to take place much earlier during the development phase of each sprint. This is how you can eliminate that key bottleneck, while also benefiting from eliminating errors earlier on.
Along with service virtualization, you have several tools to set up your automated systems and continuous integration, such as Jenkins, CruiseControl, Bamboo, and TeamCity, which all have web management interfaces. Or, you could go with a cloud solution like Amazon Pipeline Code, TravisCI, CircleCI, Codeship, and Microsoft’s Visual Studio Team Services.
One Important Note
Just having these tools in place does not ensure a successful shift and does not imply quality engineering. There are several preconditions and a level of testing maturity that must be reached in order to achieve Continuous / Agile / Shift-left testing.
For example, a precondition for test automation would be having the appropriate test environments and test data set up. Without this and several other preconditions, your shifting of QA to the left will be problematic, at the least.
Is your team ready to shift left?
Try our 9-question assessment to find out how your testing stacks up and get custom tips for your software testing strategy.
Take our software testing maturity assessment!
From Shift Left to Shift Right
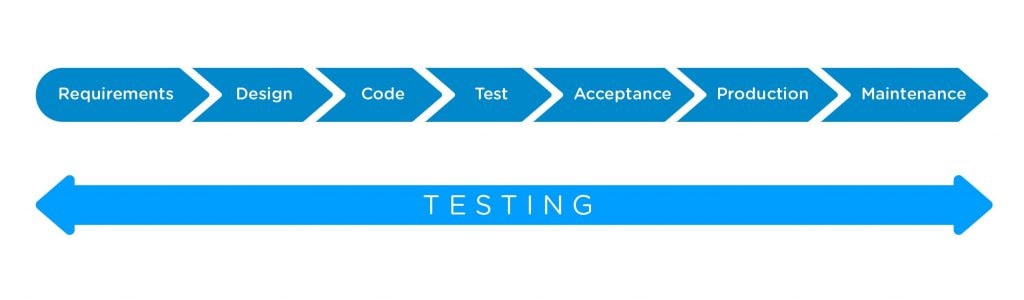

Shift left testing focuses on early defect detection, and its strength lies in the early detection of issues that could escalate into costly production failures. Yet even the best shift-left approach cannot address everything. To gain a complete view of software quality, teams also need shift right testing—validating performance, reliability, and user experience in production environments.
Shift Left vs Shift Right Testing
What’s the Difference Between Shift-Left and Shift-Right Testing?
The difference between shift-left and shift-right testing lies in when testing occurs within the software lifecycle. Shift-left testing happens earlier in development, while shift-right testing validates quality and performance in production environments. While the shift-left strategy aims to prevent issues early, the shift-right strategy focuses on learning from real user behavior once the software is live.
To dive into the topic, we share an image that helps illustrate a key shift in how we think about testing. For a long time, testing was something that happened near the end, once everything was built, as a single stage. The shift-left approach turns that idea on its head. It brings testing into the earliest stages of development, so that we can prevent issues before they even happen.
Now, you might be wondering: what about testing that happens after release? That’s where shift-right testing comes in. Instead of focusing on prevention, shift right is all about observation: seeing how the system behaves in the real world, under real conditions. It includes monitoring, A/B testing, chaos engineering, collecting feedback directly from users, and validating software quality in real-world scenarios..
Why It’s Worth Combining Shift Left Testing and Shift Right Testing
Although this article puts the spotlight on shift-left testing, especially because of its impact on catching bugs early and making collaboration more fluid, we advocate for looking at the full picture. Relying on just one approach can leave blind spots.
That’s why combining shift-left with the shift-right approach is so powerful. It lets teams build quality from the start and continue refining it once the software is live. Together, they support a continuous testing mindset that stretches across the entire development lifecycle.
If you’re curious about how to bring both sides together, we invite you to explore this article.
FAQs about Shift Left Testing

What Are The Four Types of Shift-Left Testing?
The four types of shift-left testing include traditional shift-left testing, incremental shift-left testing, Agile/DevOps, and model-based testing.
- Traditional testing: Moves functional testing to the early stages, catching issues right from the start and saving time and money down the line.
- Incremental testing: Integrates testing into each development increment, so every new feature gets tested immediately, maintaining high quality at every step.
- Agile/DevOps: Combines agile and DevOps practices for continuous testing throughout the development process. It’s like having a built-in safety net that keeps everything running smoothly as you go.
- Model-based testing: Uses models to design and run tests, catching design errors early. Think of it as having a detailed map that guides you to build everything correctly from the ground up.
What Is The Difference Between Shift-left and TDD?
Shift-left and TDD (Test-Driven Development) are complementary but distinct approaches. Shift-left is a general philosophy advocating for testing as early as possible in the development cycle. In contrast, TDD involves writing tests before the production code. In TDD, tests guide the development of the software. Shift-left, however, is broader and includes various practices and types of testing.
What Is Shift Right Testing?
Shift right testing refers to testing done in production environments to observe real user behavior and system performance. It includes practices like A/B testing, monitoring, and canary releases, helping teams validate quality after deployment and drive improvements based on real-world data.
What Is The Difference Between TDD and Shift-Right?
TDD (Test-Driven Development) and shift-right are distinct strategies. TDD focuses on writing tests before the production code to guide software development. Shift-right, on the other hand, emphasizes testing and monitoring in the production environment. While TDD aims to catch issues early in the development process, shift-right focuses on boosting quality and performance in the live environment, often using techniques like A/B testing, canary releases, and real-time monitoring.
What is Shift Left Security Testing?
Shift-left security testing integrates security checks and practices earlier in the development lifecycle. This proactive approach helps identify vulnerabilities at the design and development stages, reducing risks and improving the overall security posture of the software.
What Is an Example of Shift Left Testing?
An example of shift left is engaging testers in sprint planning to review testing requirements and detect issues before coding starts. Developers create unit tests while testers build automated integration tests, enabling continuous validation and reducing costly defects later.
How We Can Help You

With nearly 2 decades of experience and a global presence, Abstracta is a leading technology solutions company with offices in the United States, Chile, Colombia, and Uruguay. We specialize in AI-driven innovations & copilots and end-to-end software testing services.
We believe that actively bonding ties propels us further. That’s why we’ve forged robust partnerships with industry leaders like Microsoft, Datadog, Tricentis, Perforce BlazeMeter, Saucelabs, and PractiTest, empowering us to incorporate cutting-edge technologies. technologies.
Testing Maturity Model
Our software testing maturity model is a comprehensive framework that helps teams improve the quality of their software testing efforts, including all types of software testing. This model emphasizes the importance of testing early, a well-constructed test environment, and the use of reliable testing tools to meet the needs of users and stakeholders.
Processes, Technology, and People
Effective processes and tools are crucial, but they must also align with the skills and capabilities of your team members. Our approach allows us to create a well-rounded, adaptable test plan that fosters active participation and effectively meets test deliverables.
Visit our Test Strategy Services page and contact us to grow your business!

Follow us on Linkedin & X to be part of our community!
Recommended for You
Co-Development Software: A Step-by-Step Guide to Smarter Outcomes
The Complete Guide to Software Testing Outsourcing
What is Functional Testing? Types, Strategies, and Automation
Tags In


Sofía Palamarchuk, Co-CEO at Abstracta
Related Posts
We Want our DevOps Venn Diagram Circle Back – Plus One!
In this guest post, Agile test experts, Lisa Crispin and Janet Gregory, share their views on DevOps and Software Quality Close to a decade ago, the DevOps movement grew out of agile development. It was defined as the intersection of “Dev”, “Ops”, and “QA”. (Source:…
Testing as the Driver Towards a DevOps Culture
Lessons learned from helping organizations foment a DevOps culture through Agile testing practices At Abstracta we work with many companies, several of whom already have a DevOps culture and others whom we’ve helped to define and promote it. Over the years, we’ve seen DevOps gaining…
Search
Contents
Categories
- Acceptance testing
- Accessibility Testing
- AI
- API Testing
- Development
- DevOps
- Fintech
- Functional Software Testing
- Healthtech
- Mobile Testing
- Observability Testing
- Partners
- Performance Testing
- Press
- Quallity Engineering
- Security Testing
- Software Quality
- Software Testing
- Test Automation
- Testing Strategy
- Testing Tools
- Work Culture





