Is your latest fix truly ready? Get a step-by-step guide to sanity testing in software! Learn how it compares to smoke and regression testing, and how to solve common challenges with real-world solutions.


Some people see building software as assembling a complex machine, but our experience leads us to think of it more like nurturing a living organism. Each update must be carefully adjusted to keep the system healthy.
Developers face the challenge of making these adjustments without disrupting the delicate balance. By focusing on specific areas of functionality from the very beginning, sanity testing helps catch potential issues early. It allows teams to confirm that critical bug fixes or minor changes haven’t introduced new issues.
In short, it plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance between speed and quality, especially when facing tight deadlines. It saves time, reduces risks, and provides the confidence that the software is ready to thrive in its next stage.
In this guide, you’ll learn how sanity testing compares to smoke and regression testing, when to choose manual or automated approaches, and how to perform it step by step—with real-world examples and FAQs.
Our clients’ reviews on Clutch speak for themselves. Contact us and let’s grow your business!
What is Sanity Testing in Software Testing?


Sanity testing is a targeted approach to software testing that verifies specific functionalities impacted by recent updates. This type of testing is considered functional testing, as it checks that particular functions or bug fixes work as expected and have not introduced new issues. Unlike exhaustive testing methods, it focuses on a limited scope to deliver quick and efficient results.
Key Features of Sanity Testing
- Quick Validation: Prioritizes immediate feedback by concentrating on areas most likely affected by updates. This rapid approach helps maintain project timelines without sacrificing quality.
- Selective Scope: Focuses on critical functionalities rather than the entire application, enabling teams to address specific risks efficiently.
- Efficiency: Reduces the need for detailed testing across all modules, saving time and resources while promoting stability in crucial areas.
Sanity testing is a subset of regression testing, essential for maintaining software functionality without requiring more extensive testing efforts. This approach—sanity testing limited scope—proves particularly useful in agile and iterative development environments where rapid delivery is a priority.
Now that we understand the basics, let’s explore the relationship with smoke testing to clarify its unique purposes.
Enhance your software quality and mitigate business risks with our software test strategy services!
Sanity Testing vs. Smoke Testing


Although often confused, sanity testing vs smoke testing serves distinct purposes within the software development life cycle. Both methods bolster stability, but their scope and timing differ significantly.
What Is Smoke Testing?
Smoke testing is an essential testing process conducted primarily on a new software build to validate the stability of critical workflows and key functionalities. While it is often referred to as ‘build verification testing’ due to its role in verifying the readiness of a build for further testing, smoke testing is also applicable in production environments. It helps confirm that core functionalities work as expected after updates, deployments, or maintenance activities, supporting both initial validation and ongoing reliability checks.
Sanity and smoke testing complement each other. While smoke testing validates the broader stability of a build, sanity testing delves deeper into specific functionalities to verify targeted updates.
| Aspect | Sanity Testing | Smoke Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Verifies specific functionalities in a targeted area, often following changes or bug fixes. | Assesses the stability of critical workflows and key functionalities in new builds or after updates. |
| Scope | Concentrates on individual components or limited areas of the application. | Covers broad and essential workflows across the application. |
| Timing | Conducted after minor updates, fixes, or adjustments to specific functionalities. | Performed immediately after a new build or significant system updates. |
| Purpose | Identifies issues in specific areas to validate recent changes without testing unrelated parts. | Determines if the build is stable enough to proceed with in-depth testing or operate in production. |
| Focus | Targets specific changes or areas of concern for quick validation. | Verifies if the core features function correctly to support further testing. |
| Execution | Primarily manual but can include automated steps for efficiency. | Largely automated to streamline the verification process. |
| Outcome | Confirms functionality in the tested areas to address recent changes. | Validates that the build meets the basic requirements for further testing or reliable use. |
By combining both sanity and smoke testing methods, teams can validate the application’s overall functionality and specific feature reliability. Each approach complements the other, forming a robust foundation for quality assurance.
Sanity and smoke testing operate at a surface level, focusing on quick and basic test scenarios that validate functionality without detailed testing. This approach enables early detection of critical issues, providing fast feedback during the initial phase of the software development process and before production deployment.
These initial checks serve as entry points to more comprehensive testing. Once a build passes them, teams typically move on to regression or system testing to validate end-to-end functionality and ensure full system stability.
With these distinctions clear, we’ll dive into the difference between manual and automated sanity testing and learn step-by-step how to perform the overall process.
Manual vs. Automated Sanity Testing
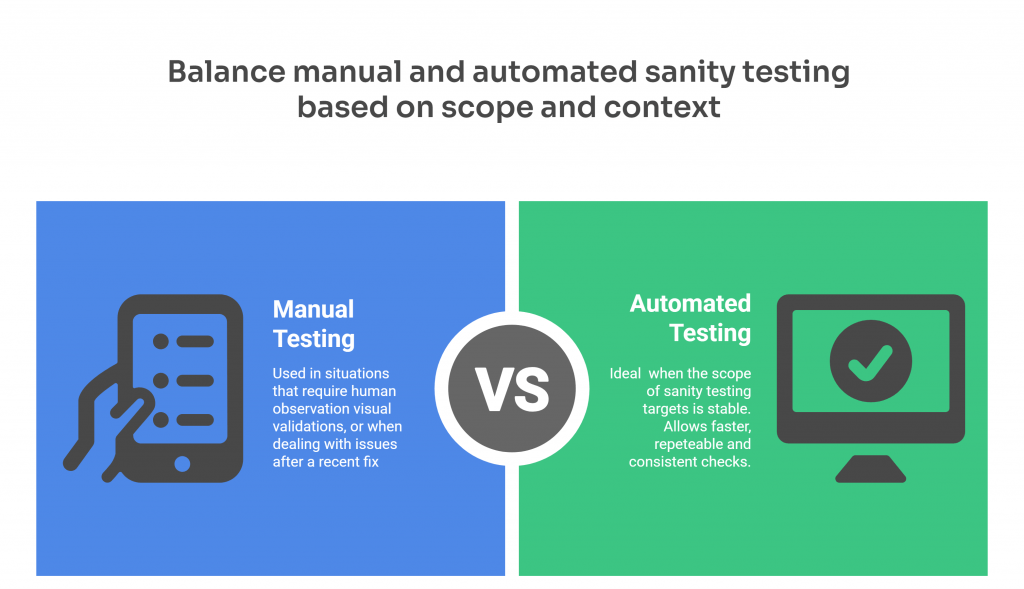

Teams can perform sanity testing either manually or through automation, depending on the complexity of the changes, available testing resources, and the timing within the testing phase.
Manual Sanity Testing
It involves executing test cases without automation tools. It is often used in situations that require human observation, when dealing with new functionalities that are still under development or critical issues after a recent fix.
This approach supports early detection of failures through quick and basic test runs, especially when time is limited. Manual testing enables flexible surface-level testing during the initial phase of the software development process, where speed is essential and not detailed testing is sufficient.
Automated Sanity Testing
On the other hand, automated sanity tests allow faster, repeatable, and more consistent execution. Automation is ideal when the scope of sanity testing targets is stable, and the same validations need to run frequently, like in integration testing pipelines or before production deployment.
By automating sanity checks across the entire application, teams speed up test results, reduce manual effort, and create room for addressing more complex testing scenarios later in the cycle. This approach is a valuable part of the broader software testing process, helping to balance coverage and agility.
Step-by-Step to Perform Effective Sanity Testing


A structured process is essential for achieving consistent and reliable results. With clear steps and proper documentation, sanity testing becomes a reliable tool for maintaining confidence in the system’s integrity.
The Sanity Testing Process
Follow these steps for efficient and reliable planning and execution:
1. Define the Scope
- Identify the modules or components affected by recent changes.
- Focus testing efforts on these areas to save time and resources.
2. Prepare Test Cases
- Design concise yet thorough test cases targeting the affected functionalities.
- Make the test cases specific and straightforward to detect potential issues.
3. Execute the Tests
- Conduct focused validations using manual or automated tools.
- Confirm that the impacted areas function as expected.
4. Analyze Results
- Review the outcomes to spot failures introduced by recent changes.
- Document findings and share them with the development team for further action.
5. Document Outcomes
- Keep detailed records of the testing process for future reference.
- Highlight any anomalies or areas that need additional testing.
6. Integrate with Regression Testing (Optional)
- Use regression tests to validate the broader impact of changes.
- This step supports a comprehensive assessment of software quality.
This process minimizes risks and optimizes the testing effort, reinforcing that the software remains stable and functional. When sanity testing fails, you may require further testing to address underlying problems and restore stability.
While the process enhances targeted validation, its integration with regression testing adds an extra layer of confidence to software quality.
Sanity Testing & Regression Testing


Sanity and regression testing are two sides of the same coin, working together to uphold software quality. Both approaches serve distinct yet complementary roles.
What is Regression Testing?
Regression testing verifies that recent changes, like updates or bug fixes, do not interfere with existing functionalities. By re-executing previous test cases, it helps confirm the application’s stability after modifications. Commonly automated, it allows teams to efficiently validate functionality across large or complex systems. To keep learning, we recommend you read our article about automated regression testing.
What Differentiates Regression Testing from Sanity Testing?
Regression takes a broad approach, re-executing a wide set of test cases to enable system-wide stability. On the other hand, sanity testing takes a narrower focus, targeting specific areas impacted by changes. It provides a quick check to confirm that recent updates work as intended and haven’t introduced new issues in those areas.
How Do Regression and Sanity Testing Complement Each Other?
Together, these approaches form a dynamic strategy. Sanity testing accelerates the testing process by pinpointing immediate risks and verifying that critical changes do not disrupt core functionalities. Once sanity testing confirms that updates are stable, regression testing takes over, examining the application as a whole. By running comprehensive test scenarios, regression testing reinforces the software’s stability and prevents regressions in complex systems.
When used effectively, sanity testing detects issues at the surface level, while regression testing dives deeper to protect the foundation. The result is a harmonious process that mitigates risks, reduces downtime, and fosters a seamless user experience.
It’s time to look at how this type of testing is applied in real situations!


Sanity testing plays a crucial role in validating specific updates and confirming that critical functionalities remain intact. Here are some concrete examples of how it can be applied to different scenarios:
Bug Fixes in Critical Features
When a critical bug is fixed in an application, such as an issue in a payment system, sanity testing verifies basic functionality and if the fix resolves the problem without introducing new issues. For instance, after fixing a flaw in transaction processing, sanity testing checks that the system can process payments without disruptions.
Hotfixes for Urgent Issues
In cases of urgent patches in production, such as addressing vulnerabilities in user authentication, sanity testing validates the stability of affected components. It checks that the fix does not cause problems in other areas, such as verifying that user accounts remain accessible and secure after the patch.
Minor Changes or Updates
When implementing small updates or enhancements, sanity testing verifies that the changes work as expected and do not affect other parts of the system. For example, after an update to the login functionality, it confirms that users can still log in normally, without encountering errors in the system.
These examples illustrate value, but hurdles remain. Even with effective examples, challenges still tend to arise.
Overcoming Challenges in Sanity Testing


In conclusion, sanity testing is a great tool, but like anything, it comes with its own challenges. Here are the most common ones, along with how you can tackle them to make the process smoother and more efficient.
1. Ambiguous Scope
- The issue: Sometimes, the scope of testing isn’t very clear, which can cause confusion about what areas to focus on. Without a clear definition, you might miss key components or waste resources on things that aren’t as critical.
- How to tackle it:
- Define the scope clearly: Identify which components or functionalities are impacted by recent changes.
- Align expectations with stakeholders: Make sure everyone, from developers to testers, is on the same page about what needs testing.
- Use a prioritization matrix to focus on the most critical parts that might have been affected by changes.
2. Tool Limitations
- The issue: Sometimes the tools you’re using don’t fully cover your testing needs, especially with more complex applications. This can lead to relying on manual testing, which takes more time and can be less reliable.
- How to tackle it:
- Leverage automation tools like Selenium or TestNG to promote faster and more efficient test execution.
- Integrate with CI/CD pipelines: Automate the testing process by integrating sanity tests into your continuous integration systems, making the entire testing lifecycle smoother.
- Create reusable test scripts: Build flexible scripts that can be reused in multiple tests, saving time and improving coverage.
3. Time Constraints
- The issue: In fast-paced development cycles, time for testing is often limited. This can lead to rushing through tests and, hopefully, not missing any important areas.
- How to tackle it:
- Prioritize key functionalities: Focus on the most important features and those likely to impact users or the business.
- Use efficient test scenarios: Instead of trying to cover everything, focus on high-impact test cases that validate the core functionalities impacted by recent changes.
- Work in parallel: Divide testing tasks among team members to speed up the process and increase efficiency.
Overcoming these challenges enables the testing team to deliver reliable software, minimizing delays. For instance, by performing sanity testing with a well-defined scope and automation tools, teams can save time while maintaining quality.
With these strategies in place, sanity testing integrates seamlessly into agile workflows, enhancing the efficiency and flexibility of development teams.
Boost your ROI with our test automation services, enhancing test efficiency and maintainability!
FAQs – Sanity Testing in Software Testing


What Is Meant by Sanity Testing?
Sanity testing is a quick check to verify that specific features still work after updates or bug fixes. Sanity testing focuses on the areas most likely impacted by those changes, helping teams detect issues early without retesting the whole system.
What Is The Difference Between Smoke and Sanity Testing?
Smoke testing evaluates the overall stability of the system, verifying if it’s ready for further testing. Sanity testing, on the other hand, concentrates on specific areas impacted by recent changes to verify they function as expected.
What Is the Difference Between Regression and Sanity Testing?
Regression testing checks the whole application to confirm nothing broke after recent changes. Sanity testing, instead, looks only at the parts that were updated, giving quick feedback without running a full suite. Sanity testing is performed when time is tight and the scope sanity testing covers is small and well-defined, unlike regression testing, which goes deeper and takes longer.
What Is an Example of a Sanity Check?
A typical sanity testing example is verifying the login functionality after a change in authentication logic. Instead of testing the entire user flow, you perform a quick validation to confirm that users can still log in successfully. This kind of shallow testing helps detect problems quickly, without diving into unrelated areas.
What to Say Instead of Sanity Check?
Some teams prefer alternatives like “quick check,” “confidence test,” or “targeted verification.” These terms are clearer, more descriptive, and better aligned with modern testing language.
What Is UAT Sanity Testing?
UAT sanity testing checks key features during user acceptance testing to verify that important updates work as expected and don’t introduce major issues before final approval.
How We Can Help You

With over 16 years of experience and a global presence, Abstracta is a leading technology solutions company with offices in the United States, Chile, Colombia, and Uruguay. We specialize in software development, AI-driven innovations & copilots, and end-to-end software testing services.
We believe that actively bonding ties propels us further. That’s why we’ve forged robust partnerships with industry leaders like Microsoft, Datadog, Tricentis, Perforce, and Saucelabs, empowering us to incorporate cutting-edge technologies.
By helping organizations like BBVA, Santander, Bantotal, Shutterfly, EsSalud, Heartflow, GeneXus, CA Technologies, and Singularity University we have created an agile partnership model for seamlessly insourcing, outsourcing, or augmenting pre-existing teams.
Our holistic approach enables us to support you across the entire software development life cycle.
Explore our solutions webpage! Contact us and join us to reshape the future of your software.

Follow us on Linkedin & X to be part of our community!
Recommended for You
How to Do Performance Testing for Web Application?
Uruguay: The Best Hub for Software QA Engineers in Latin America?
Top Performance Testing Metrics Explained
Tags In


Abstracta Team
Related Posts
What Percentage of Functional Testing Should be Automated?
Dive into the intricate world of functional testing and discover how much of it should really be automated for maximum efficiency and quality in software testing. The world of software development is ever-evolving, and the stakes for delivering high-quality, reliable software have never been higher….
Selenium vs Cypress: Which Tool Should Leaders Choose?
Compare Selenium vs Cypress from a leadership perspective. See which tool aligns with enterprise needs: scalability, compliance, speed, and long-term value.
Search
Contents
Categories
- Acceptance testing
- Accessibility Testing
- AI
- API Testing
- Development
- DevOps
- Fintech
- Functional Software Testing
- Healthtech
- Mobile Testing
- Observability Testing
- Partners
- Performance Testing
- Press
- Quallity Engineering
- Security Testing
- Software Quality
- Software Testing
- Test Automation
- Testing Strategy
- Testing Tools
- Work Culture





