Step-by-step, master performance testing for web applications with Abstracta guidance! Uncover issues early, optimize speed, and deliver outstanding user experiences.


As we discussed in this article, performance testing is a critical part of the software testing process. The collapse of software systems due to high demand damages the user experience and their digital quality of life, generating huge losses for companies.
Conducting performance tests in Web applications can make or break the user experience. You can identify and resolve performance issues before they negatively impact your users’ experience.
Imagine this: a potential customer visits your website, but it takes ages to load. They’re likely to bounce off, never to return. Performance testing enhances your web application to run smoothly.
Through this article, we aim to help you step-by-step on how to conduct performance testing in Web applications. From selecting the right tools to understanding intricate metrics, the strategies provided aim to enhance your web application’s speed, reliability, and resilience.
Looking for a performance testing partner with proven expertise?
Explore our Performance Testing Services!
Different Types of Performance Testing for Web Applications
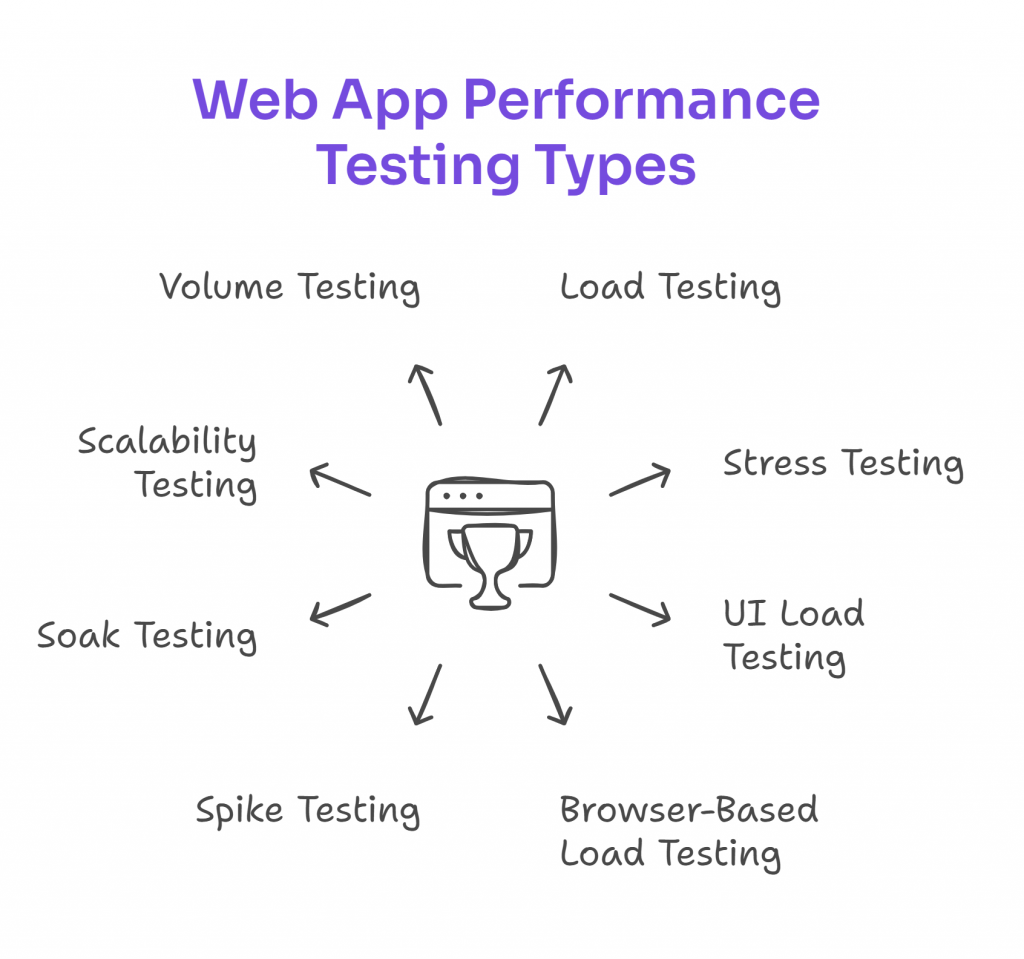

To enable optimal website performance, it’s vital to not only focus on traditional performance tests but also to understand and leverage various specialized tests.
A robust web application performance testing strategy may involve combining these specialized approaches to thoroughly test web applications and foster a seamless experience under diverse conditions.
- Load Testing: This is one of the primary facets of performance testing. Load tests simulate the expected number of concurrent users on your website to gauge if it can handle that demand while maintaining a positive user experience. A good load testing tool, combined with load generators, helps simulate user traffic and evaluate system behavior. Exploring different load test types, such as peak load or endurance testing, provides valuable insights for a robust testing strategy.
- Stress Testing: While load tests examine expected demand, stress tests push your website to its limits. They determine how much load a site can handle before it breaks down. It’s a way to find the breaking point of your website and identify its maximum operating capacity.
- UI Load Testing: As the name suggests, this focuses on the user interface under load conditions. With the increasing emphasis on single-page applications and intricate UI elements, UI load testing aims to keep your website responsive, even under a heavy load.
- Browser-Based Load Testing: In today’s digital age, users access websites from various browsers. This test evaluates if your website’s performance metrics remain consistent across browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and more.
- Spike Testing: This type of performance testing evaluates how your web application handles sudden and extreme increases in traffic. By simulating abrupt spikes in user activity, spike tests help identify vulnerabilities and assess the system’s ability to recover after such events.
- Endurance Testing: Endurance testing examines the performance of your web application under a sustained load over an extended period. This test is essential for uncovering issues like memory leaks, resource depletion, or performance degradation that may occur during prolonged usage.
- Scalability Testing: This type of performance testing evaluates how well your web application scales when resources are increased. It helps determine whether the system can handle growing demands without sacrificing speed or stability, enabling long-term resilience as your user base expands.
- Volume Testing: Volume testing assesses how your application performs when processing a large volume of data. Instead of focusing on user traffic, it examines how your system handles massive datasets, revealing potential bottlenecks related to storage, memory, or database performance.
Keep on learning in this article! Types of Performance Testing: Everything You Need to Know
Our global client reviews on Clutch speak for themselves. Contact us!
How to Conduct Performance Testing for Your Web Application


Understanding the performance of your web application is not just crucial—it’s imperative. Let’s delve into the essential steps of performance testing and aim to provide your application with the experience users anticipate and value.
1. Define Your Testing Goals
Begin with clarity and purpose. What are the primary objectives of this performance test? Setting your targets early helps direct the focus, enabling you to prioritize the most critical aspects of the application. Whether it’s improving load time, handling a specific number of concurrent users, or enhancing user satisfaction, knowing your goals will pave the way for a strategic testing approach.
2. Identify Performance Criteria
Every application has unique demands. It’s essential to discern which performance indicators will provide the most valuable insights. Therefore, determine the key performance indicators (KPIs) that matter most.
This could include metrics like response time, system throughput, and concurrent users. Establishing these criteria helps in understanding what success looks like, and enhancing your perspective on what constitutes a successful test outcome.
3. Select the Appropriate Website Performance Testing Tools
The toolset you adopt can significantly shape your testing journey. Whether it’s JMeter, LoadRunner, Gatling, or even a command line tool, your choice should align with your application’s requirements and your team’s expertise. Additionally, exploring other tools can provide flexibility and adaptability for diverse testing needs.
In the context of software development, it’s important to choose tools that support multiple protocols to cover different scenarios. These tools also allow teams to efficiently create tests that replicate real-world situations.
Tools and Techniques for Enhanced Website Performance
- Speed Test Tools: Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights not only measure page speed but also offer suggestions for improvement.
- UI Testing: With UI performance testing tools, you can help your user interface to be not just visually appealing but also fast and responsive.
- Free Tools: Several performance testing tools are available for free, providing you with insights without any initial investment.
- Resource Utilization: It’s not just about the website code. Properly optimizing your server and other resources can boost performance.
There exist open-source performance testing tools, such as Apache JMeter, and also proprietary Performance Testing Tools. Choosing the right and correct performance testing tool can make a world of difference. Not only can it bring you reduced costs, but it also may impact your performance testing activities, enhancing your agile performance testing, continuous delivery, and overall quality.
Don’t miss this article! Top Performance Testing Tools 2024 – Boost Scalability!
4. Set Up Your Testing Environment
This step is paramount. Aim for the performance testing environment to mirror your production environment as closely as possible. This includes the software, hardware, and network configurations.
By doing so, you’re optimizing the chances of uncovering real-world challenges that users might face. Every component, whether it’s the server type, OS version, or network bandwidth, can influence
5. Configure the Environment
Before plunging into tests, invest time in fine-tuning the environment. Optimize configurations for accurate testing. This includes setting the right server configurations, adjusting network settings, and aligning other infrastructure elements appropriately.
It’s crucial to pay attention to details like bandwidth limitations, server resource utilization, and potential third-party services that could influence the results. Proper configuration aims to provide a more realistic understanding of how your website will perform under various conditions. Thus, by closely emulating real-world conditions, you’re elevating the test’s authenticity and reliability.
6. Design Your Test Scenarios
Dive into the user’s shoes. Map out the actions they would undertake on your platform. Focus on identifying critical workflows within the web app – actions that users frequently carry out.
Designing your tests around these scenarios and real user behavior, as well as incorporating end to end testing, offers invaluable insights into application performance from a user’s viewpoint. Whether it’s logging in, adding items to a cart, or checkout processes on e-commerce websites, these user stories shape your testing narrative.
7. Simulate Virtual Users
A single user’s journey is just the tip of the iceberg. Beyond individual user journeys, delve into the collective user experience. Simulate varying user loads to understand how your application performs under diverse conditions.
By doing so, you’ll grasp the application’s resilience and scalability. This variability sheds light on how the application responds to both every day and peak load scenarios.
8. Execute the Tests
With the groundwork laid, it’s action time. Initiate the test execution, keeping a vigilant eye on system behaviors. Active performance monitoring during this phase helps capture key performance metrics, setting the stage for insightful analyses later on.
Incorporating backend testing during this phase allows you to evaluate the performance of server-side components, such as databases, APIs, and server configurations, which often play a critical role in overall system performance. Similarly, integration testing helps validate that different modules or services within the application interact seamlessly, identifying potential bottlenecks or inefficiencies in the communication between components.
Plus, leveraging an open-source tool can provide valuable insights while keeping costs manageable. By focusing on metrics that directly impact customer satisfaction, such as response time and error rates, you can prioritize optimizations that enhance the user experience.
9. Analyze the Results
Testing isn’t just about execution; it’s also about understanding. Post-test, immerse yourself in the data. Seek out areas causing slowdowns, component inefficiencies, or any other hindrances. This introspective phase is your guide to application optimization.
The full report generated post-testing offers a goldmine of information. But it’s not just about the numbers. It’s about understanding what they signify. For instance, if there’s a spike in load time after a specific number of users, it indicates a scalability issue. Similarly, if certain HTTP concurrent requests take longer, it may point to unoptimized queries or third-party services causing a delay.
Key performance bottlenecks can often be traced back to test data patterns, and understanding these patterns can guide optimization strategies.
Understanding Key Performance Metrics in Depth
To get a complete picture of your website’s performance, it’s essential to understand the critical metrics:
- Page Speed: Represents how quickly a web page’s content loads. With tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, one can get actionable insights into improving this metric.
- Response Time: The time it takes for a web server to respond to a user’s request. A delay here could indicate server issues or performance bottlenecks.
- HTTP Requests: These are made for every element on a site, like images and scripts. By reducing the number of requests, you can considerably improve website speed.
Want to dive into this topic? We recommend you read this article: 3 Key Performance Testing Metrics Every Tester Should Know.
10. Optimize & Reiterate
Based on insights gained, make improvements. But remember, performance tuning is iterative. Once changes are implemented, it’s back to testing. This cyclic process helps uphold performance excellence. Performance refinement is a journey, not a destination. This continuous cycle aids in maintaining and improving application robustness.
11. Scale Your Tests
Broaden your testing scope. Incorporate more simulated users, introduce tests from various global locations, and factor in diverse network conditions. Comprehensive testing aims to encompass all plausible user scenarios.
12. Consistent Monitoring
Performance doesn’t remain static. As the application evolves or as external systems morph, new challenges can arise. Committing to regular test cycles enhances the application’s preparedness for the ever-changing digital landscape. Data observability tools provide real-time insights, helping catch and resolve bottlenecks proactively
While optimizing the internal performance of your web application is critical, external factors also play a decisive role. Let’s explore how infrastructure, geolocation, and agile practices influence overall performance and testing strategies.
Revolutionize Your Testing with Abstracta Copilot! Boost productivity by 30% with our new AI-powered assistant for efficient testing.
How Do External Factors Like Infrastructure or Geolocation Affect the Performance of a Web Application?


Optimizing the internal structure of your web app is essential, but external factors can impact performance just as much. Let’s look at two key areas you should never overlook.
Server Infrastructure
The foundation of web performance begins with your server setup. Insufficient resources or misconfigurations can lead to slow response times, connection timeouts, and poor user experiences, even if your application code is highly optimized.
Investing in a scalable, well-configured infrastructure helps applications maintain speed and reliability as user demand grows. Monitoring server health and resource usage is critical to sustaining consistent performance over time.
For instance, a slow website might be the result of insufficient server resources or inadequate configurations. Even the best-optimized site can suffer if hosted on a subpar server.
Geolocation and Latency
The physical distance between the user and the server introduces latency. Simply put, the farther the data has to travel, the longer it takes for your application to load.
To mitigate this, Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) distribute your site’s content across multiple locations worldwide. By connecting users to the nearest server, CDNs minimize loading times and create faster, more responsive experiences for global audiences.
Addressing external factors is crucial to creating a strong foundation for web performance. Yet delivering consistent speed and reliability today also requires adapting performance testing practices to match modern development cycles.
Let’s explore how performance testing evolves alongside Agile and continuous delivery workflows.
Adapting Performance Testing to Agile Methodologies and Continuous Development Cycles
Modern development demands faster releases, more frequent updates, and constant user feedback. Performance testing must evolve to keep pace. Testing early and continuously is the mantra.
With each sprint or development cycle, incorporating performance tests helps pinpoint and rectify potential issues swiftly.

Testing Early and Continuously
Instead of waiting for the final stages, performance tests should begin early in the development process. Incorporating tests into every sprint helps identify performance risks before they escalate. This approach supports faster feedback loops, reducing the cost and effort of late-stage fixes.
To fully support early and continuous testing, automation becomes essential. Without it, keeping up with the pace of Agile cycles would be nearly impossible.
Leveraging Automation
When it comes to continuous testing, using automation can be a game-changer. It transforms how performance testing fits into Agile workflows. Automated test scripts can run after each code commit, validating performance alongside functionality.
By integrating these scripts into the CI/CD pipeline, performance checks become routine, not exceptional. This maintains quality without slowing down development speed.
In fact, automation is essential in Shift-Left Testing. Read this article to discover why.
Shifting Performance Left
Shift-Left Testing principles emphasize moving critical quality practices—like performance evaluation—closer to the initial stages of development.
Here,a proactive approach is key: integrate performance feedback in every sprint review. This means continuously updating performance benchmarks to track changes. Also, fostering collaboration across teams: Developers, testers, and operations teams all share responsibility for maintaining high standards.
Strengthening web application performance within agile cycles lays a solid foundation. However, delivering seamless digital experiences extends beyond the web alone. Mobile applications bring their own set of challenges—and expectations.
Not Convinced Yet About “Shift-Left Testing”? Discover its benefits and how it can transform your development process in our article
Performance Testing for Mobile Apps


Beyond web, mobile experiences demand the same level of performance—or even higher expectations. While this article focuses on web applications, performance testing is just as crucial for mobile apps. Mobile users expect fast, seamless experiences, and any delay or instability can lead to user frustration and app abandonment.
To address this, it’s important to start load testing early in the development cycle. This approach helps detect performance issues early, such as slow response times, high resource consumption, or crashes under load. Tools designed specifically for mobile performance testing simulate real-world conditions, including different network speeds, device types, and user behaviors across different devices.
Additionally, testing for mobile apps should consider factors like battery usage, memory consumption, and compatibility across various operating systems. By incorporating these tests into your strategy, you can optimize your app’s responsiveness and stability, delivering a smoother experience for users.
Performance testing for mobile apps complements the strategies discussed for web applications, highlighting the importance of a comprehensive approach to testing across platforms.
Don’t miss our Mobile App Performance Testing Guide!
How Functional Testing Complements Web Performance Testing
As discussed, performance testing is essential for both web and mobile applications to deliver fast, reliable, and seamless experiences. However, before diving into performance testing, it’s important to validate that the application’s core functionalities are working as expected. This is where functional testing becomes a key component of a comprehensive testing strategy.
By verifying that each feature of your application behaves according to its requirements, functional testing helps build a strong foundation for performance evaluations.
For instance, if a login feature or checkout process fails during test apps, it can disrupt the accuracy of performance testing results. Addressing these functional issues first allows performance tests to focus on identifying performance bottlenecks without being impacted by basic functionality problems.
Incorporating this as part of your overall testing strategy helps identify and address functional defects early, supporting a smoother transition into performance testing. This combined approach contributes to delivering an application that not only performs well under load but also aligns with user expectations in terms of functionality.
Wrapping Up – Web App Performance Testing

Performance testing is not just about digging into code or fine-tuning configurations; it’s a commitment to consistently delivering exceptional user experiences.
You already know it: Every second counts, and user patience is fleeting, so a seamlessly performing website becomes paramount. A delay of even a moment can be the line between attracting or losing a potential customer.
From selecting the right tools to understanding intricate metrics, this article provides strategies to enhance your web application’s speed, reliability, and resilience.
Keep in mind: Always prioritize optimal performance, with users at the center of your testing endeavors. Continually revisit your strategies, stay abreast of emerging trends, and utilize this step-by-step guide as a beacon.
FAQs about Web App Performance Testing

What Is Performance Testing of a Web Application?
Performance testing evaluates how web applications handle different usage conditions, such as heavy traffic or high data volumes. The goal is to detect bottlenecks, understand how the app behaves under stress, and provide users with a fast and stable experience.
How to Do Performance Testing for Web Applications?
When doing performance testing, start by defining clear objectives and user scenarios. Pick reliable tools like Apache JMeter or Gatling to simulate realistic conditions. Measure metrics such as response times, throughput, and error rates, then analyze results to detect bottlenecks and enhance user experience.
How Do You Measure the Performance of a Web Application?
Measure web application performance by tracking response times, load times, throughput, error rates, and resource consumption. Use tools like JMeter, K6, or Lighthouse for accurate analysis. These metrics reveal how your app handles user demands and where it needs improvement.
Is JMeter Used for Testing Web Application?
Yes, JMeter is commonly used to test web applications. It’s a popular tool for simulating user traffic, measuring response times, throughput, and stability. This helps teams quickly detect performance issues before users encounter them.
How to Test Performance of Web Application Manually?
Manual performance testing typically involves checking load times, responsiveness, and resource use through browser developer tools or simple timing techniques. Though helpful for initial insights, manual methods work best when complemented with automated tools for deeper analysis.
Which Testing Is Used to Test the Performance of Website?
Performance testing methods such as load testing, stress testing, endurance testing, and spike testing are ideal for evaluating website performance. These approaches reveal issues related to speed, reliability, and scalability, helping deliver a better user experience.
What Are the Best Practices for Optimizing Web Application Performance?
The best practices include prioritizing critical bottlenecks identified during testing, caching data, optimizing database queries, and compressing web assets. Leveraging tools like Google PageSpeed Insights can highlight specific areas for improvement. Additionally, offloading heavy tasks and managing third-party integrations carefully contributes to faster, more responsive performance.
How We Can Help You

With over 16 years of experience and a global presence, Abstracta is a leading technology solutions company with offices in the United States, Chile, Colombia, and Uruguay. We specialize in software development, AI-driven innovations & copilots, and end-to-end software testing services.
Our expertise spans across industries. We believe that actively bonding ties propels us further and helps us enhance our clients’ software. That’s why we’ve forged robust partnerships with industry leaders like Microsoft, Datadog, Tricentis, Perforce BlazeMeter, and Saucelabs, empowering us to incorporate cutting-edge technologies.
Embrace agility and cost-effectiveness through our Performance Testing Services!

Follow us on Linkedin & X to be part of our community!
Recommended for You
API Performance Testing: Optimize Your User Experience
Testing Applications Powered by Generative Artificial Intelligence
Web Stress Test: How to Prepare for High Traffic
Tags In


Abstracta Team
Related Posts
Preparing Your Performance Testing for 2023: 5 Challenges and Solutions
The technological and digital transformation boom of 2022 encouraged enterprises and startups to accelerate their development velocity. Consumers demanded more applications within shorter timeframes and of higher quality. What are the performance testing challenges for 2023? Find out everything in this BlazeRunner article. By Sesha…
Workload or Load Scenario in Performance Testing
In load tests we simulate the workload that an application will have in production, counting the concurrent users accessing the application, the tests cases that will be executed, and the frequency of executions by users, among other things. The concept of workload or load scenario…
Search
Contents
Categories
- Acceptance testing
- Accessibility Testing
- AI
- API Testing
- Development
- DevOps
- Fintech
- Functional Software Testing
- Healthtech
- Mobile Testing
- Observability Testing
- Partners
- Performance Testing
- Press
- Security Testing
- Software Quality
- Software Testing
- Test Automation
- Testing Strategy
- Testing Tools
- Work Culture








