How are healthcare software development solutions reshaping the future of care? From AI-powered prescriptions to interoperable systems and mobile health apps, this guide breaks down how technology is transforming healthcare delivery, decision-making, and patient experience.

Thanks to the technological advancements of recent years, software has become a cornerstone in enhancing the quality of patient care, streamlining operations, and fostering innovation.
From digitizing patient records to integrating advanced artificial intelligence systems, healthcare software applications have revolutionized how medical services are delivered and managed.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore the main applications of software in healthcare, delving into their functionalities, benefits, and the challenges they pose.
By understanding these technologies, healthcare providers can better navigate the complexities of modern healthcare delivery, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and operational efficiencies.
Looking for Custom Healthcare Software Development Services?
Enhance patient care with us!
What Is Healthcare Software Development?
Healthcare software development is the process of designing and building digital tools that improve medical services, optimize healthcare operations, and support better patient outcomes.
It combines technical expertise with deep industry knowledge to create solutions that meet regulatory standards, enable data-driven care, and adapt to evolving needs across the health sector.
Key Aspects of Healthcare Software Development
Healthcare software must go beyond functionality. It needs to be secure, usable, interoperable, and aligned with strict compliance requirements.
Key aspects include:
- Security and compliance
Adhering to HIPAA, GDPR, or PIPEDA to protect sensitive health data. - Interoperability
Enabling seamless communication across systems and care providers. - Usability and accessibility
Supporting diverse users through intuitive, inclusive design. - Scalability and performance
Handling growth while maintaining speed and reliability. - AI and automation
Driving innovation through predictive insights and workflow efficiency.
Examples of Healthcare Software Development Applications
Healthcare software can be clinical, operational, patient-facing, or AI-powered. Let’s look at how these categories are applied in practice.
Electronic Health Records (EHR)


An electronic health record (EHR) is a digital version of a patient’s medical history maintained by healthcare providers, including key clinical data such as diagnoses, medications, vital signs, and lab results. Many EHR systems include a patient portal where individuals can access their records, test results, and other relevant information.
They reduce administrative costs, improve care coordination, and enhance data mobility. However, adoption often depends on available funding, infrastructure, and trust in digital tools.
Effective EHR systems must support complete data capture, resilience, high availability, and strong security compliance. Still, challenges such as technical limitations, organizational barriers, and user resistance often hinder implementation.
With increased trust and proper adoption, EHRs can improve healthcare delivery, strengthen public health monitoring, and contribute to medical research, highlighting the broader value of healthcare information technology.
Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring


Defined as “the utilization of medical information exchanged from one site to another via electronic communications to improve a patient’s health”, telemedicine holds immense potential.
It may significantly impact the delivery of healthcare to patients, enhancing access to medical care across both urban and rural landscapes. Telemedicine platforms enhance patient communication by facilitating real-time interactions between patients and healthcare providers.
It also addresses the challenges of twenty-first-century healthcare systems, such as increased demands, aging populations, citizen mobility, global competitiveness, large amounts of information management, and the need for improved healthcare provision. All within the constraints of limited budgets and spending.
The success of telemedicine hinges on the digital readiness and competency of both patients and healthcare professionals, as well as on the regulatory frameworks that govern the exchange and use of medical data. Medical software development plays a crucial role in creating robust telemedicine platforms that enable secure and efficient communication between patients and healthcare providers.
Hospital Information Systems (HIS)
A health information system (HIS) refers to a system designed to manage healthcare data, encompassing systems that facilitate the collection, storage, management, and transmission of patient’s electronic medical records (EMR).
It also supports clinical decision-making processes, operational management in hospitals, and systems that assist in healthcare policy decisions.
These systems can improve patient outcomes, inform research, and influence policy-making and decision-making. Since HIS commonly accesses, processes, or maintains large volumes of sensitive data, maintaining strong security measures is a primary concern.
Experience our impact! Dive into our case study on how we optimized EsSalud’s performance, Peru’s premier national insurance company, through comprehensive diagnostic and technical analysis for system stabilization.
Benefits of Health Information Systems
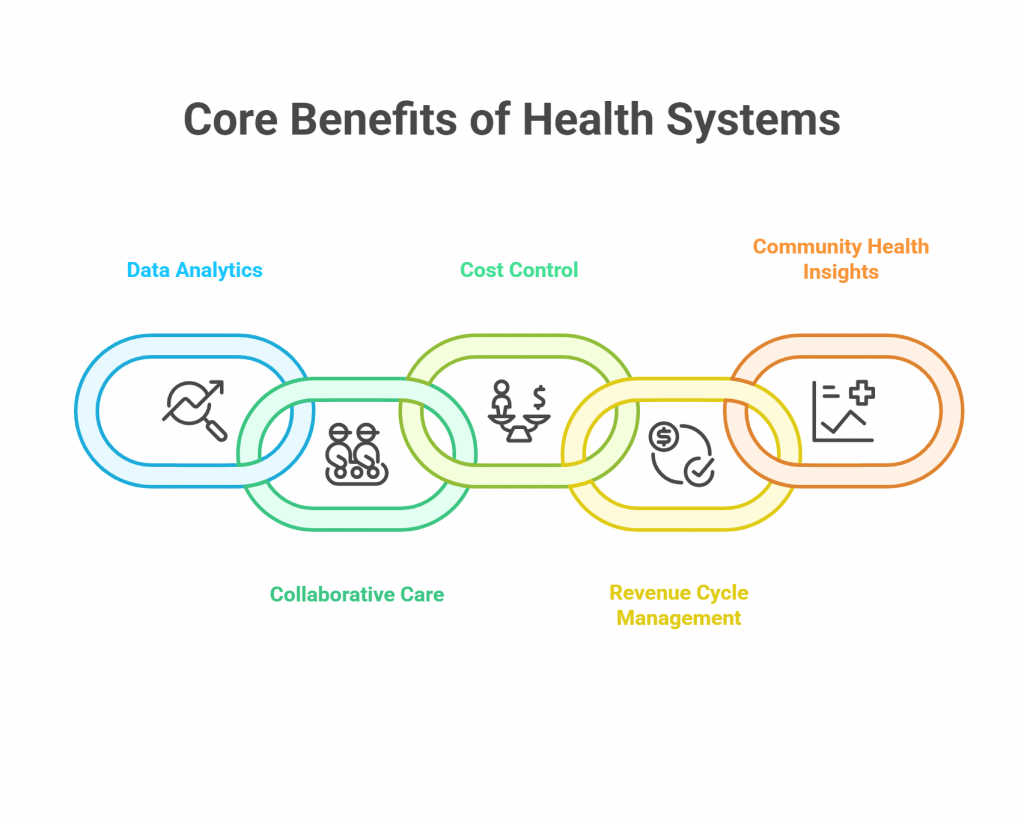

Health information systems tend to target efficiency and data management. The main drivers of health information systems are:
- Data analytics: Gather, compile, and analyze health data they constantly produce.
- Collaborative care: Allow Health information exchanges (HIEs) among different providers.
- Cost control: Use digital networks to exchange healthcare data enhances efficiency and saves costs.
- Revenue cycle management: Automate billing, manage claims, and enable prompt reimbursement for medical services, streamlining the financial operations of healthcare providers.
- Community health insights: Enable the identification of health trends within populations through the analysis of patient data, aiding in proactive healthcare delivery.
In this matter, Epic is a leading provider of large-scale implementations used in the United States and worldwide. Serves a wide spectrum of healthcare settings, from labs to urgent care.
It provides comprehensive healthcare software solutions, including EHR, patient portals, interoperability, revenue management, and analytics. This extensive reach highlights Epic‘s ability to cater to the diverse needs of different healthcare environments across the industry.
Our Clutch reviews speak for themselves.
Mobile Health Applications (mHealth)


Mobile health applications enable users to monitor their well-being, manage chronic conditions, and track physical activity and diet, empowering them to take control of their daily health.
Managing mHealth poses a challenge for the healthcare industry, requiring adaptation of systems and processes to utilize these new tools effectively.
The stringent regulations in this sector, concerning sensitive patient data and medications, present an additional hurdle to fully leveraging mobile health while complying with existing laws and regulations.
While a variety of mHealth apps exist, most operate in isolation. Integrating mHealth into existing healthcare services is a significant challenge.
Don’t miss this article! How to Take The Security of Your Mobile Apps to the Next Level of OWASP
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)

AI’s growing role in healthcare encompasses diagnosis, treatment recommendations, patient engagement, and administrative tasks.
While AI can perform human tasks effectively, large-scale adoption necessitates addressing regulations and ethical issues, such as transparency and bias.
Types of AI in Healthcare include:
- Machine Learning: Key for precision medicine, predicting treatment success, and identifying diseases. Includes neural networks and deep learning.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Used for clinical documentation and patient interaction.
- Expert Systems: Rule-based systems for clinical decision support.
- Physical Robots: Assist in surgeries and hospital logistics.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Handles repetitive administrative tasks like billing and records management.
AI will play a crucial role in precision medicine and imaging analysis. Adoption challenges include regulatory approval, EHR integration, standardization, clinician training, and funding.
Why? Because its capabilities allow for scalable, precise, and efficient analysis of vast data sets, enabling custom healthcare software development solutions on a global scale.
AI applications can manage the vast amounts of data generated in the medical field, uncovering valuable insights hidden in big medical data. Healthcare stakeholders may use AI-based tools to review historical data, predict outcomes, and identify optimal actions, making AI increasingly essential for decision-making.
Furthermore, AI-powered systems are used for remote patient treatment, prescription transcription, enhancing doctor-patient interactions, drug research and development, and patient diagnosis. So it can help healthcare organizations cut costs by deploying sophisticated, accurate technologies suited to specific functions.
AI also aids physicians by automatically identifying potential issues and alerting medical staff, thus lowering the likelihood of misdiagnoses and medical malpractice claims, which can be costly.
Real-World Example of Healthcare Software Development for Medical Prescriptions
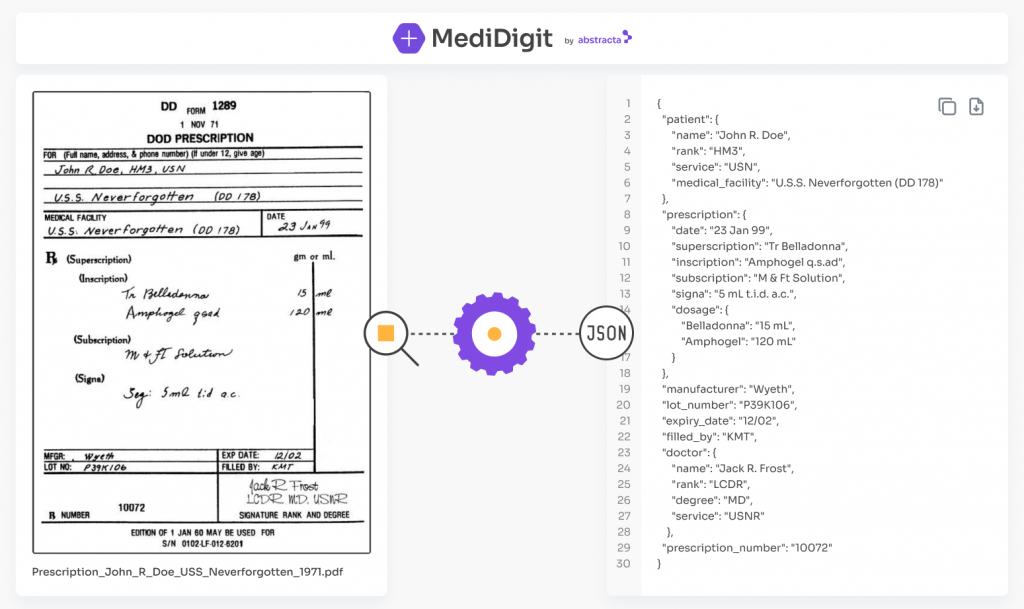

At Abstracta, we embarked on a groundbreaking project for a hospital in the U.S. that is grappling with the challenge of manually digitalizing 500 to 600 orders daily. This was not only tedious and time-consuming for their team, but also costed them 8 dollars to digitize each recipe manually.
Our project focused on the digitization of medical prescriptions with AI support. By automatically capturing critical data such as patient information, diagnosis, and details of the treating physician, Healtech aims to revolutionize the way the hospital manages its prescription orders.
In short, we revolutionized the prescription digitization process for a the hospital by implementing advanced automation tech. This transformation has allowed it to reallocate their teams to more critical tasks, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and a higher standard of care.
Some Tangible Results:
Cost Reduction
Achieved an 80X reduction in digitization costs, lowering the cost per prescription from up to $8 to $0.1.
Improved Accuracy
Maintained a 99% accuracy rate in automated information extraction, reducing the need for manual corrections.
Better Patient Care
Accelerated the digitization process, reducing patient wait times for studies and treatments, thus improving the quality of care.
We invite you to read the full case study in one click.
Interested in exploring how copilots or assistants can revolutionize your operations?
Discover our tailored solutions and see how we can transform your approach.
Compliance and Regulations in Healthcare


In the US, HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) establishes specific standards to protect patient medical information.
Covered entities, such as healthcare providers, must implement security measures to uphold key rules like Privacy, Security, and Breach Notification of protected health information (PHI).
When a cover entity engages with a business associate, such as a cloud service provider, it enters into a contract called a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) to outline permissible uses of PHI. In this line, Microsoft Azure supports HIPAA compliance; and offers a HIPAA BAA as part of the Microsoft Product Terms.
Still, it is important to mention that using Azure doesn’t automatically impart compliance to your cloud solutions. Your organization is responsible for maintaining a proper compliance process and using Azure in a way that aligns with HIPAA.
In the EU, GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and in Canada, PIPEDA (Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act), protect personal data, including health data.
Health Data Security and Privacy


Security is a critical concern in healthcare systems due to the handling of vast amounts of sensitive and confidential data. Given that medical information systems are frequently linked to both internal networks and the Internet, they are exposed to potential vulnerabilities from external devices and equipment introduced into hospital environments.
Personal health information, valued up to 50 times more than financial data, attracts cybercriminals to the healthcare sector. This attraction marks a significant shift from targeting banks and retail sectors to focusing on healthcare facilities, emphasizing the critical nature of medical data.
Ransomware attacks, where malicious software locks access to a device’s information, infrastructure, or networks until receiving a ransom, disrupt medical procedures and patient care significantly. These attacks cause treatment delays and force the redirection of care.
Furthermore, hackers manipulating medical devices can lead to false readings, incorrect medication dosages, and ultimately, endanger patient safety.
According to a National Library of Medicine (NIH) study, the growing digitization of medical care has advanced the acknowledgment of issues about secure storage, access to patients’ medical records, ownership, and medical data from associated sources.
“Every year, there are more security and privacy breaches.n 2017, more than 300 breaches were reported, and up to 37 million records were affected during 2010–2017,” the report outlines.
This urgency has only intensified with the rapid development of healthcare software solutions, bridging the gap between potential vulnerabilities and robust security measures.
Identity Theft
Identity theft is a prevalent concern, with cybercriminals exploiting stolen personal data like insurance details, names, policy numbers, birth dates, diagnosis codes, and bank information for insurance fraud, reselling medical supplies, and filing fraudulent claims.
Mitigating cyber risks and preventing unauthorized system access are critical objectives to protect patient data and maintain operational integrity.
While new healthcare approaches are feasible due to AI, new types of cyber-attacks will also become possible. These attacks may use AI systems to perform specific tasks more effectively than humans or exploit flaws in AI systems that humans cannot control.
Protect your software data! Our security testing services safeguard against cyber threats. Don’t wait for an attack; secure your systems now.
Interoperability in Health Systems


The digitalization of healthcare offers significant improvements but also faces challenges due to segregated data and legal regulations. Interoperability solutions can help overcome these challenges and reduce healthcare costs significantly through the seamless sharing of health data among providers, payers, and labs.
Interoperability enables healthcare software solutions providers access to comprehensive real-time patient data, reducing medical errors, preventing duplicate tests, and speeding up clinical decision-making. This leads to better patient care and shorter hospital stays.
Semantic Interoperability
Among the various levels of interoperability, semantic interoperability stands out because the receiving system can interpret the meaning of the sent information, even if it lacks knowledge of the sending system’s algorithms.
Standards like HL7, FHIR, DICOM, and CDA, along with terminologies like SNOMED CT, are essential for consistent data representation and interoperability in healthcare. Service-oriented architecture (SOA) further promotes interoperability by allowing services to communicate across different platforms, enhancing scalability, reliability, and efficiency.
Despite the benefits, the healthcare industry faces several barriers to achieving full interoperability. These include diverse standards, legacy systems, and resistance to digital transformation. Overcoming these challenges requires a coordinated effort to integrate comprehensive data and improve healthcare management.
Emerging Technologies in the Health Sector


As we delve into the transformative power of technologies like Blockchain, the Internet of Things (IoT), and Augmented Reality (AR) in healthcare, the innovation potential is limitless.
Each of these technologies offers unique opportunities to enhance patient care, streamline operations, and secure sensitive data.
Blockchain
Blockchain is being suggested as a powerful solution to tackle several critical challenges, particularly in securely sharing health records and safeguarding data privacy.
So, how does it work? By creating decentralized and trustless environments—this means you don’t need to rely on people or institutions for the system to function effectively. This setup is ideally suited for tasks such as automating the verification of insurance claims’ accuracy and legitimacy and managing public health data with less dependence on external parties. The result? Enhanced security and ownership of data.
However, despite its potential, blockchain adoption faces challenges such as regulatory barriers and user unfamiliarity. Organizations may invest cautiously in blockchain, and its full potential is yet to be realized. Current research is focusing on overcoming these barriers and promoting the benefits of blockchain technology.
Internet of Things (IoT)
With the rise in chronic illnesses, according to a study published by NIH, the demand for medical services has increased significantly, putting immense pressure on healthcare professionals and affecting the quality of life due to high medical costs.
Integrating the Internet of Things (IoT) into healthcare can address these challenges by improving service delivery and efficiency. “Recent developments in the health sector have consistently shown that combined technologies have the potential to improve healthcare services and assist healthcare professionals in the optimal and efficient delivery of healthcare solutions”, states the report.
How exactly can IoT help on this path?
The Internet of Things allows devices to communicate over the Internet. It offers numerous benefits, including better patient monitoring and reduced costs through technologies like RFID, sensors, and cloud computing. This integration is crucial for early disease diagnosis and intervention.
Furthermore, the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) specifically supports healthcare by enabling remote monitoring through wearable devices. These devices can help in emergencies by providing timely alerts to caregivers, improving patient outcomes.
Despite its benefits, IoT adoption in healthcare remains slow due to integration challenges and low user readiness. Successful implementation requires a structured approach to identify technological and operational needs.
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality


As stated by Mobi Health News, healthcare is experiencing a revolution with Augmented Reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies transforming surgical training, mental health care, and patient monitoring.
These technologies offer unparalleled precision and immersion, enabling hyper-realistic simulations for surgeons, 3D visualizations for accurate diagnoses, and remote monitoring for continuous care. AR and VR also provide innovative mental health therapies and encourage exercise through gamification.
While challenges like data privacy and technological disparities exist, the potential benefits for patient care and healthcare accessibility are immense, marking a significant paradigm shift in the field.
Ready to revolutionize your healthcare services with our healthcare software development solutions? software solutions and services? Contact us!
Challenges in Healthcare Software Development


Healthcare software development faces critical challenges in data handling, user experience, AI integration, and compliance. Let’s explore each of these areas in depth.
Big Data Management


Nowadays, the adoption of electronic medical records, combined with data from sensors and patient-generated information on social media, has significantly increased the volume of information healthcare systems manage. This influx encompasses the already substantial amounts of data traditionally produced in healthcare settings.
In healthcare, the flow of Big Data encompasses a wide array of information types, including clinical, biometric, financial, and scientific research data, alongside patient-provided details and social media interactions. This diversity and volume of data are ever-increasing, presenting challenges not just in terms of sheer quantity but also in the complexity of processing this information effectively.
The core issue with Big Data in healthcare lies in its unprecedented variety—different types of data, formats, and the speed at which it needs to be analyzed to continuously provide essential insights. To navigate this complexity, there’s a pressing need for advanced analytical tools and technologies capable of managing and making sense of unstructured data.
Moreover, the challenge extends beyond merely handling vast amounts of information. It involves optimizing big data storage, analysis, and the presentation of results, all within a clinical context. This requires a strategic approach that leads to data-driven decisions, enhancing patient care, and operational efficiency.
Usability and Accessibility


In the world of Health Information Technology (HIT), designing systems that are both usable and accessible to professionals and patients alike is crucial for creating effective designs. This focus helps to minimize errors and fosters the wider adoption of technological solutions. The goal here is to set clear usability standards and rigorously apply them through detailed testing methods.
As the landscape of HIT certification and design continues to evolve, embracing a user-centered approach becomes increasingly important. This approach involves thorough validation in a variety of testing environments to confirm consistency and reliability.
Manufacturers need to provide usability reports and user requirements that align with industry standards. The ultimate aim is to design HIT systems that support healthcare practitioners in delivering optimal care efficiently and safely, while also catering to diverse user needs and accessibility requirements.
To achieve these aims, it’s vital to continually customize and refine these systems based on metrics of human performance. This enables HIT systems to effectively meet the usability and accessibility objectives for users across the spectrum.
Make your healthcare software solutions accessible to all with our accessibility testing services!
Artificial Intelligence


Within healthcare innovation, Artificial Intelligence (AI) emerges as a transformative force, reshaping patient care, diagnostics, and operational workflows. The integration of AI into healthcare software heralds a new era of precision and efficiency, but also introduces a spectrum of challenges that must be meticulously addressed.
Key considerations of AI in healthcare include:
- Enhancing Patient Care: AI’s potential to refine diagnosis and treatment planning promises significant improvements in patient outcomes.
- Operational Efficiency: AI automates numerous administrative tasks, alleviating the burden on healthcare professionals and streamlining processes.
- Data Privacy and Ethics: The deployment of AI raises critical concerns regarding data privacy, ethical decision-making, and the transparency of algorithms.
- Integration Hurdles: Seamlessly incorporating AI technologies into existing healthcare infrastructures poses a complex challenge.
- Unlocking Potential: Despite these obstacles, the transformative potential of AI in healthcare is vast, offering a future of more accurate diagnoses and tailored patient care.
The path to fully harnessing AI in healthcare is fraught with hurdles, from ensuring data security and ethical integrity to achieving interoperability with current systems. As we confront these challenges, the overarching goal remains clear: to leverage AI’s capabilities to foster a healthcare environment that is more responsive, efficient, and patient-centered.
Overcoming these barriers is crucial in realizing the full promise of AI in healthcare, marking a pivotal step towards a future where technology and human expertise converge to enhance patient care and operational efficiency.
Don’t miss this article! Artificial Intelligence Business Ideas: Bring your Projects to Life
Regulatory Compliance


Navigating the landscape of regulatory compliance is essential when it comes to creating and using medical practice management software, remote patient monitoring software, health tracking apps, and medical billing software. All in all, any digital healthcare solutions for healthcare practices must align with strict standards.
The journey to maintain regulatory compliance is marked by several challenges: staying abreast of ever-changing regulations, deciphering complex legal frameworks, harmonizing compliance with the drive for innovation, fostering system interoperability, and mitigating cybersecurity risks.
Falling short of compliance standards in healthcare software development can have severe consequences, including legal penalties, damage to reputation, loss of patient trust, data breaches, fines, and the potential for litigation. These risks underscore the importance of compliance as a cornerstone for protecting both patients and healthcare organizations.
Explore the relevance of software testing in healthcare with Federico Toledo and Alan Brande on this episode of Quality Sense Podcast.
In a Nutshell


As we explore the evolving landscape of healthcare technology, it’s evident that innovations such as AI, Blockchain, and IoT are setting the stage for a transformative era in healthcare. These technologies promise to make healthcare more personalized, efficient, and accessible, revolutionizing diagnostics, treatments, and patient management.
The journey towards integrating these advancements emphasizes the importance of regulatory compliance, data security, and seamless interoperability. As technology reshapes patient care and operational workflows, it also challenges us to rethink and innovate healthcare delivery methods.
The future of healthcare software is not just about the next technological breakthrough; it’s about creating a healthcare system that is more responsive to individual needs, more efficient in its operations, and more accessible to all.
FAQs about Healthcare Software Development

What Does a Healthcare Software Developer Do?
A healthcare software developer designs, creates, and maintains software applications tailored for the healthcare industry, including EHR systems, telemedicine platforms, and medical billing software.
What Type of Software Is Used in Healthcare?
Healthcare uses various types of software, including Electronic Health Records (EHR), telemedicine platforms, Hospital Information Systems (HIS), and mobile health applications (mHealth).
How to Develop Medical Software?
Developing medical software involves understanding healthcare needs, complying with regulations, designing user-friendly interfaces, safeguarding data, and conducting continuous testing throughout the development process to meet industry standards.
What Is the SDLC in Healthcare?
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) in healthcare is a process that includes planning, designing, developing, testing, deploying, and maintaining healthcare. Testing is integrated throughout the development process to boost quality and compliance.
How Is Machine Learning Transforming Diagnostics in Healthcare Software?
Machine learning helps healthcare professionals detect patterns in patient data, improving diagnostics and accelerating decision-making in healthcare software systems.
What Are the Main Regulatory Challenges in Healthcare Software Development
Healthcare software development must comply with evolving privacy laws, regional standards, and regulatory compliance requirements while protecting sensitive medical data.
How Do Custom Healthcare Solutions Improve Patient Engagement?
Custom healthcare software solutions allow better access to records, personalized communication, and tools that support continuous patient engagement.
Why Is Interoperability Crucial in Healthcare Software Systems?
Interoperability enables seamless integration of data across healthcare software systems, improving coordination, reducing errors, and enhancing patient care.
What Cost-Saving Strategies Are Used in Developing Healthcare Apps?
Teams use modular architectures, reusable components, and cloud-based platforms to reduce costs in healthcare software product development and app delivery.
What Are the Key Features to Look for in Healthcare Practice Management Software?
Look for scheduling, billing, reporting, and secure data encryption features to support workflows and protect sensitive medical data.
How Does Telemedicine Software Enhance Access to Specialized Care?
Telemedicine software connects patients with specialists remotely, removing geographic barriers and improving access to timely, quality healthcare services.
What Role Does Healthcare Analytics Play in Optimizing Clinical Outcomes?
Healthcare data analytics supports patient data management by identifying trends to inform decisions, reduce risks, and improve clinical outcomes.
What Are Healthcare Software Systems?
These are integrated tools designed to manage medical data, support operations, and enhance care across the healthcare sector.
How We Can Help You
With over 16 years of experience and a global presence, Abstracta is a leading healthcare software development company with offices in the United States, Chile, Colombia, and Uruguay. We specialize in software development, AI-driven innovations & copilots, and end-to-end software testing services.
Our expertise spans across industries. We believe that actively bonding ties propels us further and helps us enhance our clients’ software. That’s why we’ve forged robust partnerships with industry leaders like Microsoft, Datadog, Tricentis, Perforce BlazeMeter, and Saucelabs, empowering us to incorporate cutting-edge technologies.
We invite you to learn more about our solutions and explore our case studies
Are you ready to lead the way in healthcare innovation?
Looking for custom healthcare software solutions for quality patient care?
Are you ready to lead the way in healthcare innovation?
Contact us to enhance your software quality!

Follow us on Linkedin & X to be part of our community!
Recommended for You
Generative AI in Healthcare: Unlocking New Horizons
AI for Dummies, a Powerful Guide for All
Testing Applications Powered by Generative Artificial Intelligence
Tags In


Abstracta Team
Related Posts
How Canada Can Lead Health Tech with AI-Powered Systems
What’s holding Canada’s health tech back from scaling? Explore how AI, regulation, and Abstracta Intelligence help teams deliver trusted digital solutions.
What is Data Observability? From Chaos to Clarity
Struggling with data quality issues? Uncover how data observability turns fragmented systems into trustworthy assets with real-time insight and control.
Search
Contents








